EV Shuttle Kit with HEK293 Exosomes
- Easy-to-use with a fast and straightforward loading protocol
- Introduces a wide range of biomolecules directly into isolated exosomes:
- RNAs, including siRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs
- DNAs, including plasmids
- Metabolites and other small molecules
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVS105A-1 | EV Shuttle Exosomes from HEK293 Cells | 5 Reactions | $372 |
This item has been discontinued and is no longer available. Please email customer service for assistance: info@systembio.com View substitute product 1 View substitute product 2 |
||||
| EVS110A-1 | EV Shuttle Exosomes from HEK293 Cells | 10 Reactions | $716 |
This item has been discontinued and is no longer available. Please email customer service for assistance: info@systembio.com View substitute product 1 View substitute product 2 |
||||
Overview
Overview
Putting exosomes to work: Load your cargo directly into isolated exosomes The EV Shuttle Kit harnesses a cell’s natural ability to internalize exosomes for custom cargo delivery. Each kit includes exosomes isolated from either HEK293 cells or JAWS II mouse bone marrow dendritic cells and Exo-Fect—a novel transfection reagent that enables the transfer of RNAs, DNAs (including plasmids), and small molecules directly into isolated exosomes. Use the EV Shuttle Kit for a range of applications including cargo delivery for therapeutic development, virus-free creation of stable cell lines, and gene delivery in hard-to-transfect cells. And then pair your EV Shuttle Kit with our EV-Entry Reagent to maximize cargo delivery.- Easy-to-use with a fast and straightforward loading protocol
- Introduces a wide range of biomolecules directly into isolated exosomes:
- RNAs, including siRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs
- DNAs, including plasmids
- Metabolites and other small molecules
- Enables non-viral transduction and stable cell line creation
- Provides an alternative gene delivery method for hard-to-transfect cells
References
How It Works
How It Works
Quickly and easily load cargo into isolated exosomes
Simply combine the isolated exosomes provided in the EV Shuttle Kit with Exo-Fect Reagent (also included in the Kit) and the nucleic acid or small molecule of your choice to generate exosome delivery vehicles. The Kit comes with all of the reagents you need to load cargo into exosomes and concentrate them for delivery to target cells. The protocol takes less than an hour and is highly efficient at loading cargo into exosomes for transport and delivery.
The EV Shuttle Kit is also compatible with the EV-Entry Reagent, which maximizes cargo uptake by recipient cells.
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
See the EV Shuttle System deliver cargo and alter cellular physiology even in hard-to-transfect cells
The EV Shuttle System delivers functional siRNA
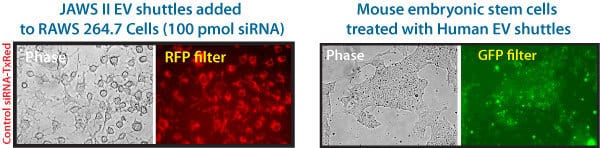
Figure 1. Mouse and Human EV Shuttles efficiently deliver siRNA to hard-to-transfect cells. (Left panel set) JAWS II mouse dendritic cell exosomes were incubated with Exo-Fect and 100 pmol Texas Red-conjugated siRNA (non-targeting control included in the EV Shuttle Kits). The siRNA-loaded EV Shuttles were then added to naive mouse monocyte macrophage cells (RAWS 264.7) in culture. The cells were imaged after 18 hours and delivery was observed as soon as 4 hours after adding the EV Shuttles. More than 80% of the recipient RAWS 264.7 cells internalized the EV Shuttle siRNA cargo.
(Right panel set) Human HEK 293 EV Shuttles were treated with SBI’s Exo-Green Kit (Cat.# EXOG200A-1) which fluorescently labels internal exosome proteins. The labeled Human EV Shuttles were then added to mouse embryonic stem cells and imaged for cargo delivery after 18 hours. The Human EV Shuttles were well-tolerated and the EVs were taken up efficiently by the mouse embryonic stem cells.
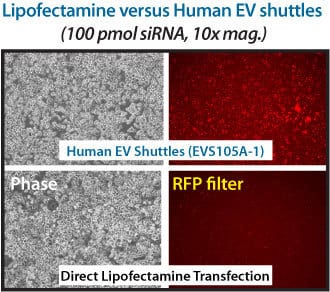
Figure 2. EV Shuttles are more efficient at delivering siRNA to hard-to-transfect cells than lipofectamine. Standard Lipofectamine transfection protocols were also compared to Human EV Shuttles on RAWS 264.7 cells using 100 pmol of Texas Red-labeled control siRNA. Fluorescence imaging shows more staining in the EV Shuttle-treated cells than the lipofectamine cells, demonstrating the higher transfection efficiency of the EV Shuttle System.
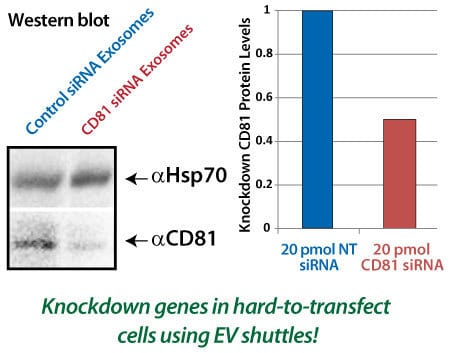
Figure 3. EV Shuttles deliver functional siRNA that can knockdown protein expression in recipient cells. Human HEK293 EV Shuttles were loaded with either an anti-CD81 siRNA or a non-targeting siRNA (NT) and then added to Mouse RAWS 264.7 cells. The cell lysates were collected after 18 hours for Western blot analysis of CD81 protein expression. EV Shuttles carrying the anti-CD81 siRNA were able to reduce CD81 protein expression in the target cells by at least 50% compared to EV Shuttles carrying the NT control siRNA.
EV Shuttles can be used as a non-viral method for generating stable cell lines
Because plasmids can be transfected into exosomes with the EV Shuttle System, EV Shuttles can be used to generate stable cell lines without the use of viruses. Here we show an example using our non-viral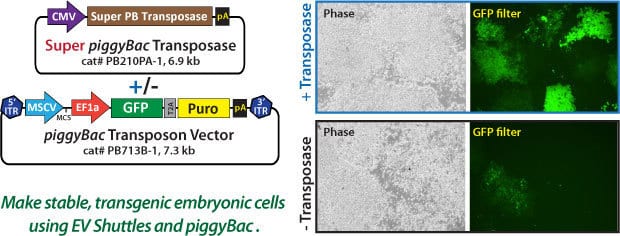
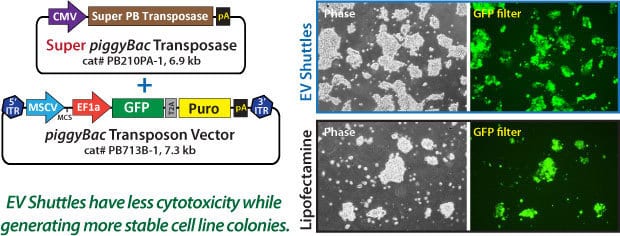
Figure 4. EV Shuttles can be used to generate stable cell lines. The Super PB Transposase Expression Plasmid (5 µg) and 5 µg of the PB713B-1 PB Transposon Vector expressing GFP and a puromycin resistance gene were loaded into Human EV Shuttles and then added to mouse embryonic stem cells in culture. ES cells were placed under 0.5 µg/mL puromycin selection for 3 days, and then 1 µg/mL puromycin for an additional 4 days of selection. As a control, EV shuttles were loaded without the Super PB Transposase Vector. Fluorescence imaging shows the successful genomic integration of Human EV Shuttle-mediated PiggyBac transposons into mouse ES cells.
Figure 5. EV Shuttles are more efficient than lipofectamine. We again used the Super PB Transposase Expression Plasmid and the PB713B-1 PB Transposon Vector expressing GFP and a puromycin resistance gene loaded into Human EV Shuttles. Loaded EV Shuttles were added to naïve HEK293 cells, and placed under puromycin selection first at 2 µg/mL for 72 hours post EV Shuttle treatment, and then at 5 µg/mL for an additional 72 hours. EV Shuttle-mediated transpositioned HEK293 cells were imaged post selection (upper panels) and compared to cells that were Lipofectamine transfected with the same PB plasmids (lower panels).
FAQs
Documentation
Citations
Related Products
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVS105A-1 | EV Shuttle Exosomes from HEK293 Cells | 5 Reactions | $372 |
This item has been discontinued and is no longer available. Please email customer service for assistance: info@systembio.com View substitute product 1 View substitute product 2 |
||||
| EVS110A-1 | EV Shuttle Exosomes from HEK293 Cells | 10 Reactions | $716 |
This item has been discontinued and is no longer available. Please email customer service for assistance: info@systembio.com View substitute product 1 View substitute product 2 |
||||
Overview
Overview
Putting exosomes to work: Load your cargo directly into isolated exosomes The EV Shuttle Kit harnesses a cell’s natural ability to internalize exosomes for custom cargo delivery. Each kit includes exosomes isolated from either HEK293 cells or JAWS II mouse bone marrow dendritic cells and Exo-Fect—a novel transfection reagent that enables the transfer of RNAs, DNAs (including plasmids), and small molecules directly into isolated exosomes. Use the EV Shuttle Kit for a range of applications including cargo delivery for therapeutic development, virus-free creation of stable cell lines, and gene delivery in hard-to-transfect cells. And then pair your EV Shuttle Kit with our EV-Entry Reagent to maximize cargo delivery.- Easy-to-use with a fast and straightforward loading protocol
- Introduces a wide range of biomolecules directly into isolated exosomes:
- RNAs, including siRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs
- DNAs, including plasmids
- Metabolites and other small molecules
- Enables non-viral transduction and stable cell line creation
- Provides an alternative gene delivery method for hard-to-transfect cells
References
How It Works
How It Works
Quickly and easily load cargo into isolated exosomes
Simply combine the isolated exosomes provided in the EV Shuttle Kit with Exo-Fect Reagent (also included in the Kit) and the nucleic acid or small molecule of your choice to generate exosome delivery vehicles. The Kit comes with all of the reagents you need to load cargo into exosomes and concentrate them for delivery to target cells. The protocol takes less than an hour and is highly efficient at loading cargo into exosomes for transport and delivery.
The EV Shuttle Kit is also compatible with the EV-Entry Reagent, which maximizes cargo uptake by recipient cells.
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
See the EV Shuttle System deliver cargo and alter cellular physiology even in hard-to-transfect cells
The EV Shuttle System delivers functional siRNA

Figure 1. Mouse and Human EV Shuttles efficiently deliver siRNA to hard-to-transfect cells. (Left panel set) JAWS II mouse dendritic cell exosomes were incubated with Exo-Fect and 100 pmol Texas Red-conjugated siRNA (non-targeting control included in the EV Shuttle Kits). The siRNA-loaded EV Shuttles were then added to naive mouse monocyte macrophage cells (RAWS 264.7) in culture. The cells were imaged after 18 hours and delivery was observed as soon as 4 hours after adding the EV Shuttles. More than 80% of the recipient RAWS 264.7 cells internalized the EV Shuttle siRNA cargo.
(Right panel set) Human HEK 293 EV Shuttles were treated with SBI’s Exo-Green Kit (Cat.# EXOG200A-1) which fluorescently labels internal exosome proteins. The labeled Human EV Shuttles were then added to mouse embryonic stem cells and imaged for cargo delivery after 18 hours. The Human EV Shuttles were well-tolerated and the EVs were taken up efficiently by the mouse embryonic stem cells.
Figure 2. EV Shuttles are more efficient at delivering siRNA to hard-to-transfect cells than lipofectamine. Standard Lipofectamine transfection protocols were also compared to Human EV Shuttles on RAWS 264.7 cells using 100 pmol of Texas Red-labeled control siRNA. Fluorescence imaging shows more staining in the EV Shuttle-treated cells than the lipofectamine cells, demonstrating the higher transfection efficiency of the EV Shuttle System.
Figure 3. EV Shuttles deliver functional siRNA that can knockdown protein expression in recipient cells. Human HEK293 EV Shuttles were loaded with either an anti-CD81 siRNA or a non-targeting siRNA (NT) and then added to Mouse RAWS 264.7 cells. The cell lysates were collected after 18 hours for Western blot analysis of CD81 protein expression. EV Shuttles carrying the anti-CD81 siRNA were able to reduce CD81 protein expression in the target cells by at least 50% compared to EV Shuttles carrying the NT control siRNA.
EV Shuttles can be used as a non-viral method for generating stable cell lines
Because plasmids can be transfected into exosomes with the EV Shuttle System, EV Shuttles can be used to generate stable cell lines without the use of viruses. Here we show an example using our non-viral
Figure 4. EV Shuttles can be used to generate stable cell lines. The Super PB Transposase Expression Plasmid (5 µg) and 5 µg of the PB713B-1 PB Transposon Vector expressing GFP and a puromycin resistance gene were loaded into Human EV Shuttles and then added to mouse embryonic stem cells in culture. ES cells were placed under 0.5 µg/mL puromycin selection for 3 days, and then 1 µg/mL puromycin for an additional 4 days of selection. As a control, EV shuttles were loaded without the Super PB Transposase Vector. Fluorescence imaging shows the successful genomic integration of Human EV Shuttle-mediated PiggyBac transposons into mouse ES cells.
Figure 5. EV Shuttles are more efficient than lipofectamine. We again used the Super PB Transposase Expression Plasmid and the PB713B-1 PB Transposon Vector expressing GFP and a puromycin resistance gene loaded into Human EV Shuttles. Loaded EV Shuttles were added to naïve HEK293 cells, and placed under puromycin selection first at 2 µg/mL for 72 hours post EV Shuttle treatment, and then at 5 µg/mL for an additional 72 hours. EV Shuttle-mediated transpositioned HEK293 cells were imaged post selection (upper panels) and compared to cells that were Lipofectamine transfected with the same PB plasmids (lower panels).