Human NKX2.5 pGreenZeo Differentiation Reporter
- Create stable myogenesis-reporting cell lines
- Monitor multiple lineages simultaneously
- Track differentiation in live cells in real time
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR10067PA-1 | Human NKX2.5 Differentiation Reporter (pGreenZeo, plasmid) | 10 µg | $1723 |
|
||||
| SR10067VA-1 | Human NKX2.5 Differentiation Reporter (pGreenZeo, virus) | >2 x 10^6 IFUs | $717 |
|
||||
Overview
Overview
Monitor myogenesis in real time
With SBI’s line of pGreenZeo, pRedZeo, and pRedTK Differentation Reporter Vectors, you can monitor stem cell differentiation in real time. These vectors leverage our reliable lentivector technology and save you time—our pre-built differentiation reporters come as ready-to-package lentivector plasmids or ready-to-transduce pre-packaged lentivirus. The Human NKX2.5 pGreenZeo Differentiation Reporter co-expresses dscGFP (destabilized copGFP, 2-hour half-life) and zeomycin resistance from the human NKX2.5 promoter/enhancer elements, enabling visualization of myogenesis using GFP fluorescence and selection for the desired cells using zeomycin.
- Create stable myogenesis-reporting cell lines
- Monitor multiple lineages simultaneously
- Track differentiation in live cells in real time
Please note that these vectors only function properly when transduced. Transfection keeps the constitutive RSV promoter intact, leading to nonspecific expression of the reporter genes.
Choose the differentiation reporter that’s right for you
Myogenic differentiation reporters
| Catalog # | Target cell type | Species | Promoter/enhancer element | Official name | Additional names |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR10010PA/VA-1 | Cardiomyocyte | Mouse | Actc | Actc1 | Cardiac muscle alpha actin 1 |
| SR10011PA/VA-1 | Cardiomyocyte | Human | MLC-2v | MYL2 | MYL2, MLC2 |
| SR10012PA/VA-1 | Cardiomyocyte | Human | TNNT2 | TNNT2 | Troponin T type 2 (cardiac), TnTC, cTnT |
| SR10013PA/VA-1 | Cardiomyocyte | Mouse | Tnnt2 | Tnnt2 | Tnt, cTnT |
| SR10014PA/VA-1 | Smooth muscle myocyte | Mouse | SM22a | Tagln | Transgelin (Tagln), SM22, Sm22a |
| SR10049PA/VA-1 | Cardiomyocyte | Human | ACTC | ACTC1 | ACTC, CMD1R |
| SR10050PA/VA-1 | Skeletal myocyte | Mouse | Myogenin | Myog | myo; MYF4 |
| Catalog # | Target cell type | Species | Promoter/enhancer element | Official name | Additional names |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR1004PA/VA-1 | B-cell | Human | B29 | CD79B | CD79b, Ig-beta, Igb, Igbeta |
| SR1005PA/VA-1 | B-cell | Mouse | B29 | Cd79b | Cd79b |
| SR1006PA/VA-1 | CD8 T-cell | Mouse | CD8 | Cd8a | BB154331, Ly-2, Ly-35, Ly-B, Lyt-2 |
| SR1007PA/VA-1 | Erythroid | Human | HLA-DRa | HLA-DRA | HLA-DRA1, major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR alpha |
| SR1008PA/VA-1 | Macrophage, microglia | Mouse | Cd68 | Cd68 | macrosialin, Scard1, gp110 |
| SR1009PA/VA-1 | Pan T-cell | Human | CD2 | CD2 | SRBC, T11 |
| SR10032PA/VA-1 | Lymphocyte | Human | LCK | LCK | YT16, p56lck, pp58lck |
| Catalog # | Target cell type | Species | Promoter/enhancer element | Official name | Additional names |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR1008PA/VA-1 | Macrophage, microglia | Mouse | Cd68 | Cd68 | macrosialin, Scard1, gp110 |
| SR10015PA/VA-1 | Astrocyte | Human | GFAP | GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| SR10016PA/VA-1 | Astrocyte | Mouse | Gfap | Gfap | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| SR10017PA/VA-1 | Microglia | Human | CD11b | ITGAM | integrin, alpha M, CD11B, CR3A, MAC-1, MAC1A, MGC117044, MO1A |
| SR10018PA/VA-1 | Microglia | Mouse | EMR1 | Emr1 | EGF-like module containing, mucin-like, hormone receptor-like sequence 1, EGF-TM7, F4/80 |
| SR10019PA/VA-1 | Microglia | Mouse | Iba-1 | Aif1 | allograft inflammatory factor 1 (Aif-1), ionized calcium binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba-1) |
| SR10020PA/VA-1 | Muller glia | Mouse | Cd44 | Cd44 | HERMES, Ly-24, Pgp-1 |
| SR10021PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Human | BM88 | Cend1 | cell cycle exit and neuronal differentiation 1 (Cend1) |
| SR10022PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Mouse | Camk2a | Camk2a | CaMK II; alpha-CaMKII |
| SR10023PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Mouse | GAD67 | Gad1 | glutamic acid decarboxylase 1, EP10, GAD67, Gad-1 |
| SR10024PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Rat | NSE | Eno2 | enolase 2, gamma (Eno2), neuron-specific enolase (NSE) |
| SR10025PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Mouse | Ta1 a-tubulin | Tuba1a | tubulin, alpha 1A (Tuba1a), Tuba-1, Tuba1 |
| SR10026PA/VA-1 | Oligodendrocyte | Mouse | MBP | Mbp | myelin basic protein (Mbp), myelin deficient; shiverer |
| SR10027PA/VA-1 | Photoreceptor | Human | Opsin | OPN1SW | opsin 1 (cone pigments), short-wave-sensitive (color blindness, tritan) |
| SR10034PA/VA-1 | Neural Stem Cell | Rat | Nestin | Nes | Nes |
| SR10035PA/VA-1 | Neural Stem Cell | Human | Nestin | NES | NES |
| SR10041PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Human | Doublecortin | DCX | DBCN, DC, LISX, SCLH, XLIS |
| SR10047PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Human | MAP2 | MAP2 | MAP2A, MAP2B, MAP2C |
| SR10048PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Human | FABP7 | FABP7 | B-FABP, BLBP, DKFZp547J2313, FABPB, MRG |
| Catalog # | Target cell type | Species | Promoter/enhancer element | Official name | Additional names |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR1001PA/VA-1 | Chondrocyte | Mouse | Col2a1 | Col2a1 | collagen, type II, alpha 1 |
| SR1002PA/VA-1 | Osteoblast | Human | SPP1 | SPP1 | secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1), osteopontin (OPN) |
| SR1003PA/VA-1 | Osteoblast | Human | Osteocalcin | BGLAP | bone gamma-carboxyglutamate (BGLAP), BGP, PMF1 |
| SR10036PA/VA-1 | Adipocyte | Mouse | ALBP | Fabp4 | 422/aP2, ALBP/Ap2, Ap2, Lbpl |
| SR10038PA/VA-1 | Epithelium | Human | Keratin 14 | KRT14 | CK14, EBS3, EBS4, K14, NFJ |
| Catalog # | Target cell type | Species | Promoter/enhancer element | Official name | Additional names |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR10028PA/VA-1 | Beta cell | Human | Insulin | INS | insulin |
| SR10037PA/VA-1 | Islet | Human | NGN3 | NGN3 | neurogenin 3, Atoh5, Math4B, bHLHa7, neurog3 |
| SR10039PA/VA-1 | Islet | Human | PDX1 | PDX1 | IDX-1, IPF1, IUF1, MODY4, PDX-1, STF-1 |
| SR10040PA/VA-1 | Islet | Mouse | Pdx1 | Pdx1 | IDX-1, IPF-1, Ipf1, Mody4, STF-1, pdx-1 |
References
How It Works
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
See some of our differentiation reporters in action
SBI’s differentiation reporters are used in a number of papers. The data shown below are just one example (from Ravin R, Hoeppner DJ, Munno DM, Carmel L, Sullivan J, Levitt DL, Miller JL, Athaide C, Panchision DM, McKay RD. Potency and fate specification in CNS stem cell populations in vitro. Cell Stem Cell. 2008 Dec 4; 3(6):670-80. PMID: 19041783)
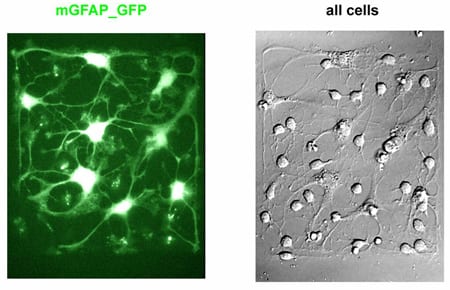
Figure 1. Live imaging of neuronal differentiation. Ravin, et al, used SBI’s Human GFAP pGreenFire Differentiation Reporter (Cat.# SR10016VA-1), which drives GFP expression from the glial fibrillary acidic protein promoter, to watch human neural stem cells differentiate into a network of mature neurons, oligodendrocytes, and astrocytes over the course of seven days. The periodic “flashes” seen in this video correspond to fluorescent photos taken of the growing cells to identify the GFP signals. The final photo taken after the network formation is shown below the video (color added). Among the network of neurons, only the astrocytes are bright green, demonstrating the specificity of SBI’s human GFAP pGreenFire Differentiation Reporter.
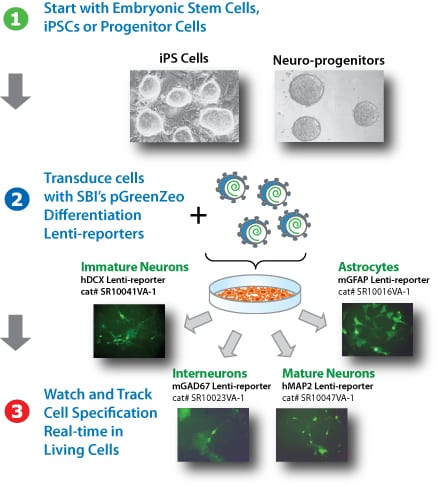
Figure 2. Simultaneously track multiple lineages from iPS and progenitor cells.
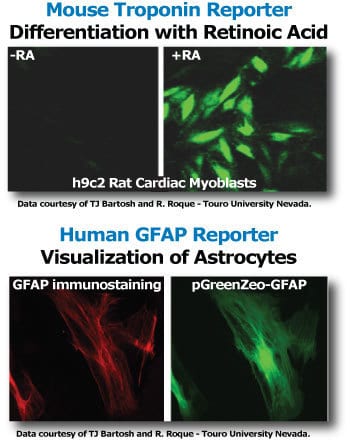
Figure 3. Additional differentiation reporter data.
FAQs
Resources
Citations
Related Products
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR10067PA-1 | Human NKX2.5 Differentiation Reporter (pGreenZeo, plasmid) | 10 µg | $1723 |
|
||||
| SR10067VA-1 | Human NKX2.5 Differentiation Reporter (pGreenZeo, virus) | >2 x 10^6 IFUs | $717 |
|
||||
Overview
Overview
Monitor myogenesis in real time
With SBI’s line of pGreenZeo, pRedZeo, and pRedTK Differentation Reporter Vectors, you can monitor stem cell differentiation in real time. These vectors leverage our reliable lentivector technology and save you time—our pre-built differentiation reporters come as ready-to-package lentivector plasmids or ready-to-transduce pre-packaged lentivirus. The Human NKX2.5 pGreenZeo Differentiation Reporter co-expresses dscGFP (destabilized copGFP, 2-hour half-life) and zeomycin resistance from the human NKX2.5 promoter/enhancer elements, enabling visualization of myogenesis using GFP fluorescence and selection for the desired cells using zeomycin.
- Create stable myogenesis-reporting cell lines
- Monitor multiple lineages simultaneously
- Track differentiation in live cells in real time
Please note that these vectors only function properly when transduced. Transfection keeps the constitutive RSV promoter intact, leading to nonspecific expression of the reporter genes.
Choose the differentiation reporter that’s right for you
Myogenic differentiation reporters
| Catalog # | Target cell type | Species | Promoter/enhancer element | Official name | Additional names |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR10010PA/VA-1 | Cardiomyocyte | Mouse | Actc | Actc1 | Cardiac muscle alpha actin 1 |
| SR10011PA/VA-1 | Cardiomyocyte | Human | MLC-2v | MYL2 | MYL2, MLC2 |
| SR10012PA/VA-1 | Cardiomyocyte | Human | TNNT2 | TNNT2 | Troponin T type 2 (cardiac), TnTC, cTnT |
| SR10013PA/VA-1 | Cardiomyocyte | Mouse | Tnnt2 | Tnnt2 | Tnt, cTnT |
| SR10014PA/VA-1 | Smooth muscle myocyte | Mouse | SM22a | Tagln | Transgelin (Tagln), SM22, Sm22a |
| SR10049PA/VA-1 | Cardiomyocyte | Human | ACTC | ACTC1 | ACTC, CMD1R |
| SR10050PA/VA-1 | Skeletal myocyte | Mouse | Myogenin | Myog | myo; MYF4 |
| Catalog # | Target cell type | Species | Promoter/enhancer element | Official name | Additional names |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR1004PA/VA-1 | B-cell | Human | B29 | CD79B | CD79b, Ig-beta, Igb, Igbeta |
| SR1005PA/VA-1 | B-cell | Mouse | B29 | Cd79b | Cd79b |
| SR1006PA/VA-1 | CD8 T-cell | Mouse | CD8 | Cd8a | BB154331, Ly-2, Ly-35, Ly-B, Lyt-2 |
| SR1007PA/VA-1 | Erythroid | Human | HLA-DRa | HLA-DRA | HLA-DRA1, major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR alpha |
| SR1008PA/VA-1 | Macrophage, microglia | Mouse | Cd68 | Cd68 | macrosialin, Scard1, gp110 |
| SR1009PA/VA-1 | Pan T-cell | Human | CD2 | CD2 | SRBC, T11 |
| SR10032PA/VA-1 | Lymphocyte | Human | LCK | LCK | YT16, p56lck, pp58lck |
| Catalog # | Target cell type | Species | Promoter/enhancer element | Official name | Additional names |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR1008PA/VA-1 | Macrophage, microglia | Mouse | Cd68 | Cd68 | macrosialin, Scard1, gp110 |
| SR10015PA/VA-1 | Astrocyte | Human | GFAP | GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| SR10016PA/VA-1 | Astrocyte | Mouse | Gfap | Gfap | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| SR10017PA/VA-1 | Microglia | Human | CD11b | ITGAM | integrin, alpha M, CD11B, CR3A, MAC-1, MAC1A, MGC117044, MO1A |
| SR10018PA/VA-1 | Microglia | Mouse | EMR1 | Emr1 | EGF-like module containing, mucin-like, hormone receptor-like sequence 1, EGF-TM7, F4/80 |
| SR10019PA/VA-1 | Microglia | Mouse | Iba-1 | Aif1 | allograft inflammatory factor 1 (Aif-1), ionized calcium binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba-1) |
| SR10020PA/VA-1 | Muller glia | Mouse | Cd44 | Cd44 | HERMES, Ly-24, Pgp-1 |
| SR10021PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Human | BM88 | Cend1 | cell cycle exit and neuronal differentiation 1 (Cend1) |
| SR10022PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Mouse | Camk2a | Camk2a | CaMK II; alpha-CaMKII |
| SR10023PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Mouse | GAD67 | Gad1 | glutamic acid decarboxylase 1, EP10, GAD67, Gad-1 |
| SR10024PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Rat | NSE | Eno2 | enolase 2, gamma (Eno2), neuron-specific enolase (NSE) |
| SR10025PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Mouse | Ta1 a-tubulin | Tuba1a | tubulin, alpha 1A (Tuba1a), Tuba-1, Tuba1 |
| SR10026PA/VA-1 | Oligodendrocyte | Mouse | MBP | Mbp | myelin basic protein (Mbp), myelin deficient; shiverer |
| SR10027PA/VA-1 | Photoreceptor | Human | Opsin | OPN1SW | opsin 1 (cone pigments), short-wave-sensitive (color blindness, tritan) |
| SR10034PA/VA-1 | Neural Stem Cell | Rat | Nestin | Nes | Nes |
| SR10035PA/VA-1 | Neural Stem Cell | Human | Nestin | NES | NES |
| SR10041PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Human | Doublecortin | DCX | DBCN, DC, LISX, SCLH, XLIS |
| SR10047PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Human | MAP2 | MAP2 | MAP2A, MAP2B, MAP2C |
| SR10048PA/VA-1 | Neuron | Human | FABP7 | FABP7 | B-FABP, BLBP, DKFZp547J2313, FABPB, MRG |
| Catalog # | Target cell type | Species | Promoter/enhancer element | Official name | Additional names |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR1001PA/VA-1 | Chondrocyte | Mouse | Col2a1 | Col2a1 | collagen, type II, alpha 1 |
| SR1002PA/VA-1 | Osteoblast | Human | SPP1 | SPP1 | secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1), osteopontin (OPN) |
| SR1003PA/VA-1 | Osteoblast | Human | Osteocalcin | BGLAP | bone gamma-carboxyglutamate (BGLAP), BGP, PMF1 |
| SR10036PA/VA-1 | Adipocyte | Mouse | ALBP | Fabp4 | 422/aP2, ALBP/Ap2, Ap2, Lbpl |
| SR10038PA/VA-1 | Epithelium | Human | Keratin 14 | KRT14 | CK14, EBS3, EBS4, K14, NFJ |
| Catalog # | Target cell type | Species | Promoter/enhancer element | Official name | Additional names |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR10028PA/VA-1 | Beta cell | Human | Insulin | INS | insulin |
| SR10037PA/VA-1 | Islet | Human | NGN3 | NGN3 | neurogenin 3, Atoh5, Math4B, bHLHa7, neurog3 |
| SR10039PA/VA-1 | Islet | Human | PDX1 | PDX1 | IDX-1, IPF1, IUF1, MODY4, PDX-1, STF-1 |
| SR10040PA/VA-1 | Islet | Mouse | Pdx1 | Pdx1 | IDX-1, IPF-1, Ipf1, Mody4, STF-1, pdx-1 |
References
How It Works
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
See some of our differentiation reporters in action
SBI’s differentiation reporters are used in a number of papers. The data shown below are just one example (from Ravin R, Hoeppner DJ, Munno DM, Carmel L, Sullivan J, Levitt DL, Miller JL, Athaide C, Panchision DM, McKay RD. Potency and fate specification in CNS stem cell populations in vitro. Cell Stem Cell. 2008 Dec 4; 3(6):670-80. PMID: 19041783)
Figure 1. Live imaging of neuronal differentiation. Ravin, et al, used SBI’s Human GFAP pGreenFire Differentiation Reporter (Cat.# SR10016VA-1), which drives GFP expression from the glial fibrillary acidic protein promoter, to watch human neural stem cells differentiate into a network of mature neurons, oligodendrocytes, and astrocytes over the course of seven days. The periodic “flashes” seen in this video correspond to fluorescent photos taken of the growing cells to identify the GFP signals. The final photo taken after the network formation is shown below the video (color added). Among the network of neurons, only the astrocytes are bright green, demonstrating the specificity of SBI’s human GFAP pGreenFire Differentiation Reporter.
Figure 2. Simultaneously track multiple lineages from iPS and progenitor cells.
Figure 3. Additional differentiation reporter data.