pFC-CMV-GFP-SV40-Neo Positive Control Donor Vector
- Non-viral transgene delivery
- Single-copy integration
- Preferential integration at active sites
- Delivery of inserts with no size constraints
- Easy generation of cell lines
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC520A-1 | pFC-CMV-GFP-SV40-Neo Positive Control Donor Vector | 10 µg | $759 |
|
||||
Overview
Overview
One-step, non-viral, single-copy transgenesis
Use the GFP-delivering pFC-CMV-GFP-SV40-Neo Positive Control Donor Vector as a positive control for your PhiC31 Integrase System-based genome engineering projects. Simply co-transfect with the PhiC31 Integrase Expression Plasmid (Cat.# FC200PA-1) and select for integrants using neomycin resistance as well as fluorescence imaging to detect GFP expression.

The PhiC31 Integrase System
Popularly used for gene therapy development and related applications, one of the major advantages of SBI’s PhiC31 system is the tight control over copy number—the majority of clones that undergo integration events have single insertions (Supporting Data, Figure 1), reducing the risks of insertional mutagenesis effects.
Other benefits include:
- Non-viral transgene delivery
- Single-copy integration
- Preferential integration at active sites
- Delivery of inserts with no size constraints
- Easy generation of cell lines
When you want non-viral gene delivery, have a large insert, and/or need controlled, single-copy genomic integration, turn to the PhiC31 Integrase System.
References
How It Works
How It Works
One-step transgene delivery with the PhiC31 Integrase System
With the PhiC31 Integrase System, you simply clone your gene-of-interest into the attB Donor Plasmid, and then (Step 1) co-transfect with a PhiC31 Integrase Expression Plasmid. (Inside the cell) The PhiC31 Integrase is transiently expressed, and mediates site-specific recombination between the attB site on the donor plasmid and a pseudo attP site in the genome. (Result) Because pseudo attP sites are typically present in transcriptionally active sites of the genome, your gene-of-interest will likely be integrated into an active region of the genome.
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Streamlined gene delivery with the PhiC31 Integrase System
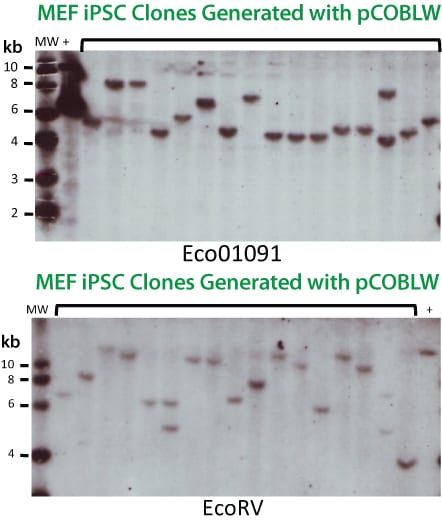
Figure 1. With the PhiC31 Integrase System, the majority of clones that undergo integration events have single insertions. Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from positive clones co-transfected with both the PhiC31 Integrase Expression Plasmid (Cat.# FC200PA-1) and the pCOBLW (CAG-Oct4-Sox2-Klf4-Myc-GFP-SV40-Neo) Mouse Reprogramming PhiC31 Donor Plasmid shows the copy number status for 16 different iPSC lines. With both restriction enzymes used, 14 out of 16 lines show single insertions (88%) demonstrating the tight copy number control possible with the PhiC31 Integrase System.
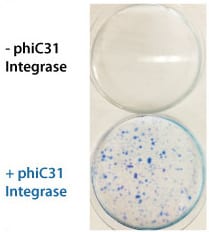
Figure 2. The PhiC31 Integrase System efficiently introduces a puromycin resistance marker to HEK293 cells. The dual promoter PhiC31 Donor Vector pFC-PGK-MCS-EF1-GFP-Puro (Cat.# FC551A-1) was co-transfected into HEK293 cells with either carrier DNA (top plate) or the PhiC31 Integrase Expression Plasmid (bottom plate) and the cells placed under puromycin selection after three days. After an additional eleven days, the cells were fixed and stained with a solution of 50% methanol plus 1% methylene blue to image colonies. Only the cells co-transfected with integrase formed colonies (bottom panel), demonstrating the high efficiency of the PhiC31 Integrase System for transgene delivery.
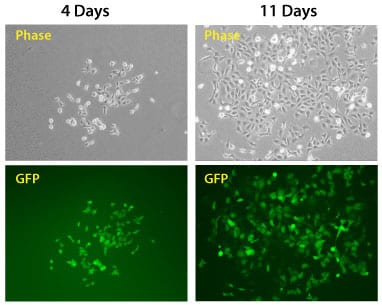
Figure 3. The PhiC31 Integrase System efficiently introduces a puromycin resistance marker and GFP to HEK293 cells. The dual promoter PhiC31 Donor Vector pFC-PGK-MCS-EF1-GFP-Puro (Cat.# FC551A-1) was co-transfected into HEK293 cells with the PhiC31 Integrase Expression Plasmid (bottom plate), the cells placed under puromycin selection after two days, and cells imaged after another four and eleven days. Comparison of phase versus fluorescence imaging shows that the majority of cells robustly express the GFP reporter.
FAQs
Documentation
Citations
Related Products
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC520A-1 | pFC-CMV-GFP-SV40-Neo Positive Control Donor Vector | 10 µg | $759 |
|
||||
Overview
Overview
One-step, non-viral, single-copy transgenesis
Use the GFP-delivering pFC-CMV-GFP-SV40-Neo Positive Control Donor Vector as a positive control for your PhiC31 Integrase System-based genome engineering projects. Simply co-transfect with the PhiC31 Integrase Expression Plasmid (Cat.# FC200PA-1) and select for integrants using neomycin resistance as well as fluorescence imaging to detect GFP expression.

The PhiC31 Integrase System
Popularly used for gene therapy development and related applications, one of the major advantages of SBI’s PhiC31 system is the tight control over copy number—the majority of clones that undergo integration events have single insertions (Supporting Data, Figure 1), reducing the risks of insertional mutagenesis effects.
Other benefits include:
- Non-viral transgene delivery
- Single-copy integration
- Preferential integration at active sites
- Delivery of inserts with no size constraints
- Easy generation of cell lines
When you want non-viral gene delivery, have a large insert, and/or need controlled, single-copy genomic integration, turn to the PhiC31 Integrase System.
References
How It Works
How It Works
One-step transgene delivery with the PhiC31 Integrase System
With the PhiC31 Integrase System, you simply clone your gene-of-interest into the attB Donor Plasmid, and then (Step 1) co-transfect with a PhiC31 Integrase Expression Plasmid. (Inside the cell) The PhiC31 Integrase is transiently expressed, and mediates site-specific recombination between the attB site on the donor plasmid and a pseudo attP site in the genome. (Result) Because pseudo attP sites are typically present in transcriptionally active sites of the genome, your gene-of-interest will likely be integrated into an active region of the genome.
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Streamlined gene delivery with the PhiC31 Integrase System
Figure 1. With the PhiC31 Integrase System, the majority of clones that undergo integration events have single insertions. Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from positive clones co-transfected with both the PhiC31 Integrase Expression Plasmid (Cat.# FC200PA-1) and the pCOBLW (CAG-Oct4-Sox2-Klf4-Myc-GFP-SV40-Neo) Mouse Reprogramming PhiC31 Donor Plasmid shows the copy number status for 16 different iPSC lines. With both restriction enzymes used, 14 out of 16 lines show single insertions (88%) demonstrating the tight copy number control possible with the PhiC31 Integrase System.
Figure 2. The PhiC31 Integrase System efficiently introduces a puromycin resistance marker to HEK293 cells. The dual promoter PhiC31 Donor Vector pFC-PGK-MCS-EF1-GFP-Puro (Cat.# FC551A-1) was co-transfected into HEK293 cells with either carrier DNA (top plate) or the PhiC31 Integrase Expression Plasmid (bottom plate) and the cells placed under puromycin selection after three days. After an additional eleven days, the cells were fixed and stained with a solution of 50% methanol plus 1% methylene blue to image colonies. Only the cells co-transfected with integrase formed colonies (bottom panel), demonstrating the high efficiency of the PhiC31 Integrase System for transgene delivery.
Figure 3. The PhiC31 Integrase System efficiently introduces a puromycin resistance marker and GFP to HEK293 cells. The dual promoter PhiC31 Donor Vector pFC-PGK-MCS-EF1-GFP-Puro (Cat.# FC551A-1) was co-transfected into HEK293 cells with the PhiC31 Integrase Expression Plasmid (bottom plate), the cells placed under puromycin selection after two days, and cells imaged after another four and eleven days. Comparison of phase versus fluorescence imaging shows that the majority of cells robustly express the GFP reporter.