PinPoint Integrase Expression Plasmid
- Create isogenic cell lines
- Achieve high-efficiency integration with no insert size-limit
- Turn cell line construction into a high-throughput process
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIN200A-1 | PinPoint Integrase Expression Plasmid | 10 µg | $739 |
|
||||
Overview
Overview
Easy and efficient isogenic cell line creation
Powering the PinPoint Targeted Integration System is the PinPoint Integrase, a hyper-specific and efficient enzyme that catalyzes integration of a PinPoint Donor Vector at a PinPoint attP site. Because the PinPoint Integrase does not recognize any attP sites in the genome, you must first insert a PinPoint attP site. As long as only one PinPoint attP site is placed, the PinPoint Integrase will insert a single copy of the PinPoint Donor Vector, making this system ideal for applications that require single copy integration at a defined site, such as isogenic cell line creation.

With the PinPoint Targeted Integration System, you can ensure that only a single copy of your transgene is inserted into the genome.
- Create isogenic cell lines
- Achieve high-efficiency integration with no insert size-limit
- Turn cell line construction into a high-throughput process
References
How It Works
How It Works
Targeted integration with the PinPoint System
Engineering cells with the PinPoint Targeted Integration System is a two-step process:
- Insertion of the PinPoint placement site (PinPoint attP) into the target genome using either the PhiC31 Integrase, which preferentially inserts into transcriptionally active sites of the genome, or the CRISPR/Cas9 System for insertion into a defined locus, such as the AAVS1 Safe Harbor Site.
- Integration of a PinPoint Vector into the pre-placed attP site. Integration is mediated by the PinPoint Integrase, which mediates a recombination event between the PinPoint attB site (located on the PinPoint Vector) and the PinPoint attP site (placed into the target genome in step 1). Because the PinPoint Integrase only recognizes your pre-placed PinPoint attP site, you get very stringent control of integration location.
A third optional step involves removal of extra vector sequences using the Cre/Lox system, leaving behind only your expression cassette and a single LoxP site.
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
See the PinPoint Targeted Integration System in action
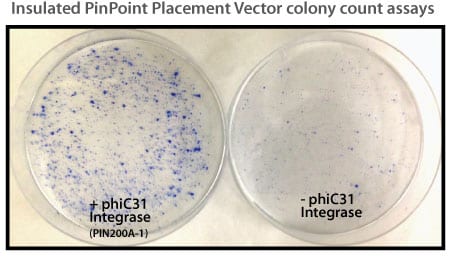
Figure 1. Efficient placement of the PinPoint attP site using the PhiC31 System. Step 1 of the PinPoint Targeted Integration System—the PinPoint attP site was placed into HEK293 cells using the PinPoint-FC Placement Vector (Cat.# PIN300A-1) and the PhiC31 Integrase (Cat.# FC200PA-1). Positive cells were selected with G418 (neomycin resistance) for fourteen days and six separate lines were picked and expanded. After eleven days, the cells were fixed and stained with a solution of 50% methanol plus 1% methylene blue. The plates were washed twice with PBS and allowed to air dry. Only the plate of cells that were transfected with the PhiC31 Integrase Expression Plasmid showed a robust number of cells.
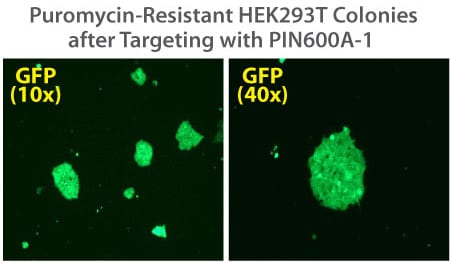
Figure 2. Targeted integration with the PinPoint Integrase and a PinPoint Donor Plasmid. Step 2 of the PinPoint Targeted Integration System—the cell lines created in Figure 1 were transfected with a Positive Control PinPoint Gene Donor Vector expressing GFP (Cat.# PIN600A-1) for precise integration. Unlike the R4 integrase used in a similar system, the PinPoint Integrase does not recognize pseudo-sites and will only integrate at its placed recognition sequence. This feature results in the increased efficiency of correctly retargeted cell lines compared to the R4 integrase system. The entire therapeutic gene expression cassette is active and fully insulated with cHS4 DNA elements.
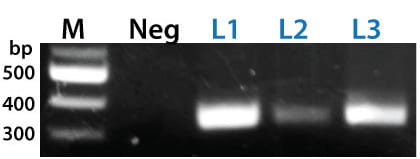
Figure 3. The PinPoint Integrase mediated specific placement of the PinPoint Donor Vector. We used a junction PCR assay to verify that the PinPoint Donor Vector was integrated at the correct site targeted to the correct site, amplifying across the PinPoint attL site (after PinPoint mediated integration, the plasmid-borne PinPoint attP and attB sites become genomic attL and attR sites). The appearance of bands in the L1, L2, and L3 lanes only indicate the predicted, PinPoint Integrase-mediated insertion of the PIN600A-1 Donor Vector at the placed PinPoint attP site with high precision.
FAQs
Documentation
Citations
Related Products
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIN200A-1 | PinPoint Integrase Expression Plasmid | 10 µg | $739 |
|
||||
Overview
Overview
Easy and efficient isogenic cell line creation
Powering the PinPoint Targeted Integration System is the PinPoint Integrase, a hyper-specific and efficient enzyme that catalyzes integration of a PinPoint Donor Vector at a PinPoint attP site. Because the PinPoint Integrase does not recognize any attP sites in the genome, you must first insert a PinPoint attP site. As long as only one PinPoint attP site is placed, the PinPoint Integrase will insert a single copy of the PinPoint Donor Vector, making this system ideal for applications that require single copy integration at a defined site, such as isogenic cell line creation.

With the PinPoint Targeted Integration System, you can ensure that only a single copy of your transgene is inserted into the genome.
- Create isogenic cell lines
- Achieve high-efficiency integration with no insert size-limit
- Turn cell line construction into a high-throughput process
References
How It Works
How It Works
Targeted integration with the PinPoint System
Engineering cells with the PinPoint Targeted Integration System is a two-step process:
- Insertion of the PinPoint placement site (PinPoint attP) into the target genome using either the PhiC31 Integrase, which preferentially inserts into transcriptionally active sites of the genome, or the CRISPR/Cas9 System for insertion into a defined locus, such as the AAVS1 Safe Harbor Site.
- Integration of a PinPoint Vector into the pre-placed attP site. Integration is mediated by the PinPoint Integrase, which mediates a recombination event between the PinPoint attB site (located on the PinPoint Vector) and the PinPoint attP site (placed into the target genome in step 1). Because the PinPoint Integrase only recognizes your pre-placed PinPoint attP site, you get very stringent control of integration location.
A third optional step involves removal of extra vector sequences using the Cre/Lox system, leaving behind only your expression cassette and a single LoxP site.
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
See the PinPoint Targeted Integration System in action
Figure 1. Efficient placement of the PinPoint attP site using the PhiC31 System. Step 1 of the PinPoint Targeted Integration System—the PinPoint attP site was placed into HEK293 cells using the PinPoint-FC Placement Vector (Cat.# PIN300A-1) and the PhiC31 Integrase (Cat.# FC200PA-1). Positive cells were selected with G418 (neomycin resistance) for fourteen days and six separate lines were picked and expanded. After eleven days, the cells were fixed and stained with a solution of 50% methanol plus 1% methylene blue. The plates were washed twice with PBS and allowed to air dry. Only the plate of cells that were transfected with the PhiC31 Integrase Expression Plasmid showed a robust number of cells.
Figure 2. Targeted integration with the PinPoint Integrase and a PinPoint Donor Plasmid. Step 2 of the PinPoint Targeted Integration System—the cell lines created in Figure 1 were transfected with a Positive Control PinPoint Gene Donor Vector expressing GFP (Cat.# PIN600A-1) for precise integration. Unlike the R4 integrase used in a similar system, the PinPoint Integrase does not recognize pseudo-sites and will only integrate at its placed recognition sequence. This feature results in the increased efficiency of correctly retargeted cell lines compared to the R4 integrase system. The entire therapeutic gene expression cassette is active and fully insulated with cHS4 DNA elements.
Figure 3. The PinPoint Integrase mediated specific placement of the PinPoint Donor Vector. We used a junction PCR assay to verify that the PinPoint Donor Vector was integrated at the correct site targeted to the correct site, amplifying across the PinPoint attL site (after PinPoint mediated integration, the plasmid-borne PinPoint attP and attB sites become genomic attL and attR sites). The appearance of bands in the L1, L2, and L3 lanes only indicate the predicted, PinPoint Integrase-mediated insertion of the PIN600A-1 Donor Vector at the placed PinPoint attP site with high precision.