Exo-FBS
- Exosome-sized vesicles removed
- Very low levels of CD63-positive bovine exosomes
- Undetectable levels of bovine miRNAs
- Comparable growth rates as standard FBS
- Interchangeable with standard FBS (add 10% in DMEM or RPMI)
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXO-FBS-250A-1 | Exosome-depleted FBS Media Supplement | 250 mL | $1259 |
|
||||
| EXO-FBS-50A-1 | Exosome-depleted FBS Media Supplement | 50 mL | $293 |
|
||||
Overview
Overview
Avoid inadvertently studying bovine exosomes
Fetal bovine serum, or FBS, is an important component of many types of cell culture media. But for researchers interested in isolating exosomes from cultured cells, standard FBS can introduce unwanted complications—bovine exosomes, which can cause significant background issues or interfere with functional studies. Which is why SBI developed Exo-FBS, our patented exosome-depleted FBS.- Exosome-sized vesicles removed
- Very low levels of CD63-positive bovine exosomes
- Undetectable levels of bovine miRNAs
- Comparable growth rates as standard FBS
- Interchangeable with standard FBS (add 10% in DMEM or RPMI)
References
How It Works
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
High quality and great performance
Exo-FBS supports robust cell growth (Figure 1), has greatly reduced levels of bovine exosomes (Figures 2), and bovine miRNAs (Figure 3). Cell growth in media supplemented with Exo-FBS is similar to cell growth in media supplemented with standard FBS (Figure 1).
Exo-FBS supports more robust cell growth health than competitors
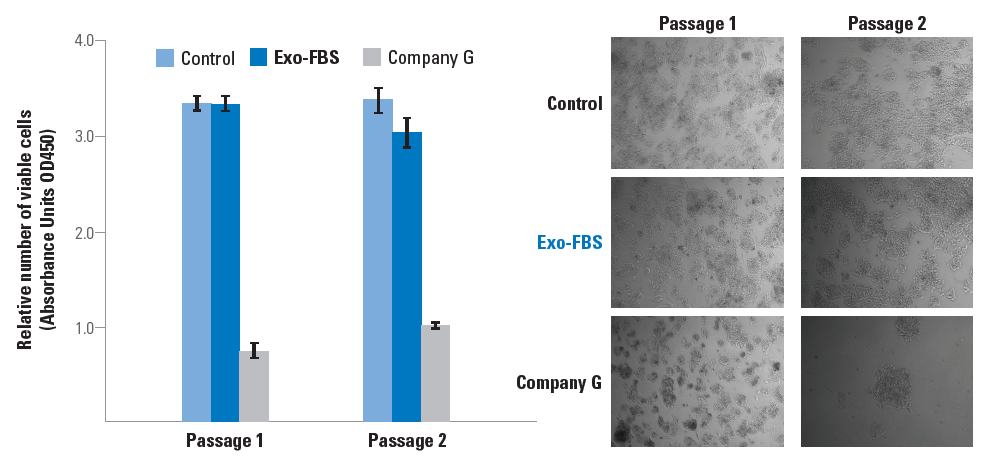
Figure 1. Exo-FBS supports more robust cell growth than Company G’s exosome-depleted FBS. HepG2 cells were grown in media containing either standard FBS (control), Exo-FBS, or Company G’s exosome-depleted FBS. Data is shown after one and two passages and illustrates that Exo-FBS provides a higher number of viable cells (left panel, viability assessed using a CCK-8 assay) and a healthier cell morphology (right panel) than Company G’s product.
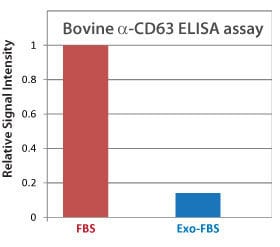
Figure 2. Bovine α-CD63 ELISA shows low levels of exosomes in Exo-FBS CD63 is an exosome-specific marker. An α-CD63 ELISA of standard FBS and Exo-FBS shows very low levels of CD63 in Exo-FBS, supporting the NTA data, which showed low numbers of exosome-sized particles in Exo-FBS (Figure 1). Equal volumes (50 µl) of either standard FBS or Exo-FBS depleted media supplement were used and the graphed results normalized to the signal level of standard FBS.
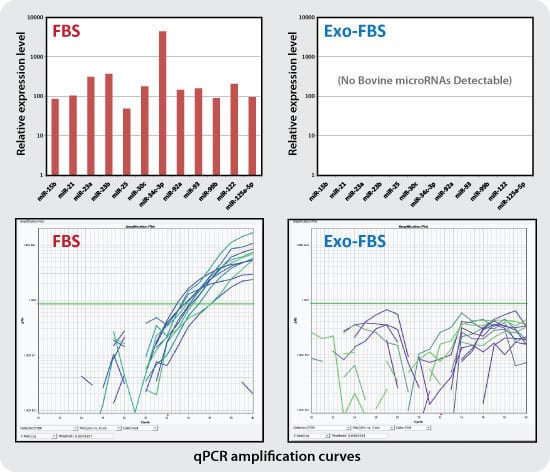
Figure 3. qPCR assays show undetectable levels of bovine exosomal miRNAs in Exo-FBS. While standard FBS contains amplifiable miRNAs (12 of the 72 individual miRNAs tested, left panels), Exo-FBS shows no amplifiable miRNAs (right panels). Standard FBS and Exo-FBS media supplements (4 ml) were treated with Trizol extraction methods to recover exosomal RNAs. RNA was converted to cDNA and 72 individual bovine microRNAs were measured by qPCR using SBI’s QuantiMir system.
FAQs
Documentation
Citations
Related Products
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXO-FBS-250A-1 | Exosome-depleted FBS Media Supplement | 250 mL | $1259 |
|
||||
| EXO-FBS-50A-1 | Exosome-depleted FBS Media Supplement | 50 mL | $293 |
|
||||
Overview
Overview
Avoid inadvertently studying bovine exosomes
Fetal bovine serum, or FBS, is an important component of many types of cell culture media. But for researchers interested in isolating exosomes from cultured cells, standard FBS can introduce unwanted complications—bovine exosomes, which can cause significant background issues or interfere with functional studies. Which is why SBI developed Exo-FBS, our patented exosome-depleted FBS.- Exosome-sized vesicles removed
- Very low levels of CD63-positive bovine exosomes
- Undetectable levels of bovine miRNAs
- Comparable growth rates as standard FBS
- Interchangeable with standard FBS (add 10% in DMEM or RPMI)
References
How It Works
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
High quality and great performance
Exo-FBS supports robust cell growth (Figure 1), has greatly reduced levels of bovine exosomes (Figures 2), and bovine miRNAs (Figure 3). Cell growth in media supplemented with Exo-FBS is similar to cell growth in media supplemented with standard FBS (Figure 1).
Exo-FBS supports more robust cell growth health than competitors
Figure 1. Exo-FBS supports more robust cell growth than Company G’s exosome-depleted FBS. HepG2 cells were grown in media containing either standard FBS (control), Exo-FBS, or Company G’s exosome-depleted FBS. Data is shown after one and two passages and illustrates that Exo-FBS provides a higher number of viable cells (left panel, viability assessed using a CCK-8 assay) and a healthier cell morphology (right panel) than Company G’s product.
Figure 2. Bovine α-CD63 ELISA shows low levels of exosomes in Exo-FBS CD63 is an exosome-specific marker. An α-CD63 ELISA of standard FBS and Exo-FBS shows very low levels of CD63 in Exo-FBS, supporting the NTA data, which showed low numbers of exosome-sized particles in Exo-FBS (Figure 1). Equal volumes (50 µl) of either standard FBS or Exo-FBS depleted media supplement were used and the graphed results normalized to the signal level of standard FBS.
Figure 3. qPCR assays show undetectable levels of bovine exosomal miRNAs in Exo-FBS. While standard FBS contains amplifiable miRNAs (12 of the 72 individual miRNAs tested, left panels), Exo-FBS shows no amplifiable miRNAs (right panels). Standard FBS and Exo-FBS media supplements (4 ml) were treated with Trizol extraction methods to recover exosomal RNAs. RNA was converted to cDNA and 72 individual bovine microRNAs were measured by qPCR using SBI’s QuantiMir system.