XPack CMV-XP-RFP-EF1α-Puro Expression Lentivector
- Powerful—enables a wealth of applications, including
- Exosome labeling
- Exosome cargo tracking
- Exosomes as cargo delivery vehicles
- Exosomes as biotherapeutics
- Exosome-generating stable cell lines with protein cargo-of-interest
- Optimized—SBI developed the XPack peptide tag for robust exosome targeting
- Reliable—based on SBI’s highly-cited, well-proven lentivector technology
- Versatile
- Two promoter options for expression in a wide range of cells
- Comes as pre-built reporters (GFP, RFP, luciferase) or ready-to-customize cloning lentivectors
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XPAK531PA-1 | XPack CMV-XP-RFP-EF1α-Puro Expression Lentivector | 10 µg | $819 |
|
||||
Overview
Overview
Label exosomes with RFP using XPack™Easily create stable cell lines that produce RFP-labeled exosomes with the XPack CMV-XP-RFP-EF1α-Puro Expression Lentivector. Take advantage of SBI’s well-proven lentivector technology to express RFP from the strong CMV promoter (also available with an MSCV promoter for expression in hematopoietic and stem cells) and the optimized XPack exosome targeting tag to package RFP into exosomes.
The XPack System at a glance:
- Powerful—enables a wealth of applications, including
- Exosome labeling
- Exosome cargo tracking
- Exosomes as cargo delivery vehicles
- Exosomes as biotherapeutics
- Exosome-generating stable cell lines with protein cargo-of-interest
- Optimized—SBI developed the XPack peptide tag for robust exosome targeting
- Reliable—based on SBI’s highly-cited, well-proven lentivector technology
- Versatile
- Two promoter options for expression in a wide range of cells
- Comes as pre-built reporters (GFP, RFP, luciferase) or ready-to-customize cloning lentivectors
| Reporter | CMV Promoter (For most cell lines) | MSCV Promoter (For hematopoietic and stem cell lines) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Customize with our cloning vector |
||||
| XPAK510PA-1 | XPack CMV-XP-MCS-EF1α-Puro | XPAK710PA-1 | XPack MSCV-XP-MCS-EF1α-Puro | |
Label exosomes with pre-built reporters |
||||
| GFP | XPAK530CL-1 XPAK530PA-1 XPAK530VA-1 | XPack CMV-XP-GFP-EF1α-Puro | XPAK730PA-1 XPAK730VA-1 | XPack MSCV-XP-GFP-EF1α-Puro |
| RFP | XPAK531PA-1 | XPack CMV-XP-RFP-EF1α-Puro | ||
| Luciferase | XPAK532CL-1 XPAK532PA-1 XPAK532VA-1 | XPack CMV-XP-Luciferase-EF1α-Puro | XPAK732PA-1 XPAK732VA-1 | XPack MSCV-XP-Luciferase-EF1α-Puro |
References
How It Works
How It Works
Optimized for success
With XPack, SBI has developed an optimized N-terminal peptide sequence that targets the peptide—and any protein fused to it—to the inner surface of the exosome membrane. Our pre-built XPack-reporter constructs come in GFP, RFP, and luciferase options to cover a wide range of labeling needs.
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
XPack efficiently packages GFP into exosomes which can be used to deliver GFP to target cells
Part 1: Packaging GFP into exosomes with XPack
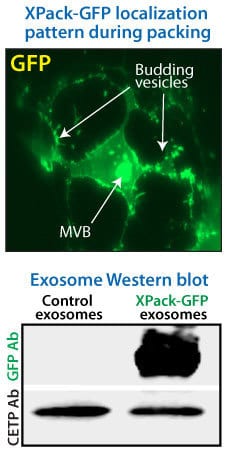
The XPack-GFP fusion protein is efficiently packaged as exosome cargo and delivered to target cells. HEK-293 cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding an N-terminal XPack-GFP fusion protein (Cat.# XPAK530PA-1). Twenty-four hours later, GFP localization patterns were visualized on a Leica DMI300B fluorescent microscope (Figure 1, upper panel). GFP expression patterns within transfected cells demonstrate a localization pattern characteristic of exosomal loading, with punctate spots along the cell periphery indicating budding vesicles and a brightly fluorescent spot in the cell interior corresponding to the multivesicular body (MVB), the site of exosome assembly and maturation prior to secretion.
After 48 hours, exosomes were isolated using ExoQuick-TC® and analyzed for GFP via Western blot (Figure 1, lower panel). Equal amounts of exosomal lysates (15 µg) were separated on gradient SDS PAGE gels and detected for GFP protein expression. The control for exosome loading was an anti-CETP antibody. XPack-GFP exosomes had very high amounts of GFP protein loaded as cargo.
Figure 1. XPack efficiently packages GFP into exosomes. (Upper panel) XPack-GFP localization during packaging. (Lower panel) Western blot showing robust loading of GFP into the isolated exosomes.
Part 2: XPack-GFP Exosome Delivery to Target Cells
The XPack-GFP exosomes isolated as described above were then added to recipient HEK-293 cells to test for GFP delivery. Cells exposed to XPack-GFP exosomes were imaged by fluorescent microscopy, which showed subcellular GFP localization consistent with endocytosis of the XPack-GFP exosomes and delivery of the XPack-GFP protein cargo into the cell (Figure 2, left panels). Subsequently, these recipient cells were washed twice with PBS and cellular lysates were prepared for Western blot analysis using anti-GFP antibodies. Anti-GAPDH was used as a cellular protein loading control. The Western blot data further verified the successful delivery of GFP proteins to recipient cells via the XPack exosome engineering technology (Figure 2, right panel).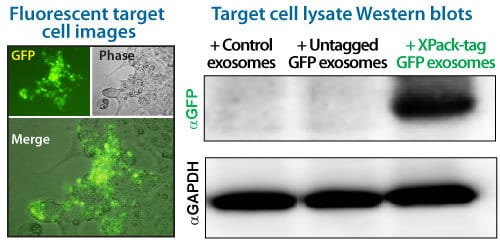
Figure 2. XPack-GFP exosomes deliver GFP to target cells. (Left panel) XPack-GFP localization during packaging. (Right panel) Western blot showing robust GFP delivery to target cells.
FAQs
Documentation
Citations
Related Products
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XPAK531PA-1 | XPack CMV-XP-RFP-EF1α-Puro Expression Lentivector | 10 µg | $819 |
|
||||
Overview
Overview
Label exosomes with RFP using XPack™Easily create stable cell lines that produce RFP-labeled exosomes with the XPack CMV-XP-RFP-EF1α-Puro Expression Lentivector. Take advantage of SBI’s well-proven lentivector technology to express RFP from the strong CMV promoter (also available with an MSCV promoter for expression in hematopoietic and stem cells) and the optimized XPack exosome targeting tag to package RFP into exosomes.
The XPack System at a glance:
- Powerful—enables a wealth of applications, including
- Exosome labeling
- Exosome cargo tracking
- Exosomes as cargo delivery vehicles
- Exosomes as biotherapeutics
- Exosome-generating stable cell lines with protein cargo-of-interest
- Optimized—SBI developed the XPack peptide tag for robust exosome targeting
- Reliable—based on SBI’s highly-cited, well-proven lentivector technology
- Versatile
- Two promoter options for expression in a wide range of cells
- Comes as pre-built reporters (GFP, RFP, luciferase) or ready-to-customize cloning lentivectors
| Reporter | CMV Promoter (For most cell lines) | MSCV Promoter (For hematopoietic and stem cell lines) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Customize with our cloning vector |
||||
| XPAK510PA-1 | XPack CMV-XP-MCS-EF1α-Puro | XPAK710PA-1 | XPack MSCV-XP-MCS-EF1α-Puro | |
Label exosomes with pre-built reporters |
||||
| GFP | XPAK530CL-1 XPAK530PA-1 XPAK530VA-1 | XPack CMV-XP-GFP-EF1α-Puro | XPAK730PA-1 XPAK730VA-1 | XPack MSCV-XP-GFP-EF1α-Puro |
| RFP | XPAK531PA-1 | XPack CMV-XP-RFP-EF1α-Puro | ||
| Luciferase | XPAK532CL-1 XPAK532PA-1 XPAK532VA-1 | XPack CMV-XP-Luciferase-EF1α-Puro | XPAK732PA-1 XPAK732VA-1 | XPack MSCV-XP-Luciferase-EF1α-Puro |
References
How It Works
How It Works
Optimized for success
With XPack, SBI has developed an optimized N-terminal peptide sequence that targets the peptide—and any protein fused to it—to the inner surface of the exosome membrane. Our pre-built XPack-reporter constructs come in GFP, RFP, and luciferase options to cover a wide range of labeling needs.
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
XPack efficiently packages GFP into exosomes which can be used to deliver GFP to target cells
Part 1: Packaging GFP into exosomes with XPack
The XPack-GFP fusion protein is efficiently packaged as exosome cargo and delivered to target cells. HEK-293 cells were transfected with a plasmid encoding an N-terminal XPack-GFP fusion protein (Cat.# XPAK530PA-1). Twenty-four hours later, GFP localization patterns were visualized on a Leica DMI300B fluorescent microscope (Figure 1, upper panel). GFP expression patterns within transfected cells demonstrate a localization pattern characteristic of exosomal loading, with punctate spots along the cell periphery indicating budding vesicles and a brightly fluorescent spot in the cell interior corresponding to the multivesicular body (MVB), the site of exosome assembly and maturation prior to secretion.
After 48 hours, exosomes were isolated using ExoQuick-TC® and analyzed for GFP via Western blot (Figure 1, lower panel). Equal amounts of exosomal lysates (15 µg) were separated on gradient SDS PAGE gels and detected for GFP protein expression. The control for exosome loading was an anti-CETP antibody. XPack-GFP exosomes had very high amounts of GFP protein loaded as cargo.
Figure 1. XPack efficiently packages GFP into exosomes. (Upper panel) XPack-GFP localization during packaging. (Lower panel) Western blot showing robust loading of GFP into the isolated exosomes.
Part 2: XPack-GFP Exosome Delivery to Target Cells
The XPack-GFP exosomes isolated as described above were then added to recipient HEK-293 cells to test for GFP delivery. Cells exposed to XPack-GFP exosomes were imaged by fluorescent microscopy, which showed subcellular GFP localization consistent with endocytosis of the XPack-GFP exosomes and delivery of the XPack-GFP protein cargo into the cell (Figure 2, left panels). Subsequently, these recipient cells were washed twice with PBS and cellular lysates were prepared for Western blot analysis using anti-GFP antibodies. Anti-GAPDH was used as a cellular protein loading control. The Western blot data further verified the successful delivery of GFP proteins to recipient cells via the XPack exosome engineering technology (Figure 2, right panel).
Figure 2. XPack-GFP exosomes deliver GFP to target cells. (Left panel) XPack-GFP localization during packaging. (Right panel) Western blot showing robust GFP delivery to target cells.