EF1α-RFP-U6-gRNA(SA) Two Vector AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease™ gRNA Expression Plasmid
- Deliver Cas9 in vivo
- Edit genomes in post-natal animals
- Develop gene therapies in small animal models
- Generate novel disease models
- Choose from All-in-one or Two Vector AAV-Cas9 systems
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASAAV300PA-1 | gRNA expression vector for the Two Vector AAV SmartNuclease System, linearized AAV plasmid (EF1α-RFP-U6-gRNA(SA)) | 10 Reactions | $669 |
|
||||
Overview
Overview
Expanding your genome editing capabilities with our flexible AAV Two Vector System
Bringing together the versatile CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing system with powerful recombinant AAV (rAAV) technology, SBI’s AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease™ vectors extend genome editing capabilities to cutting edge in vivo applications.

For situations where you would like to introduce saCas9 and gRNA separately, SBI offers a Two Vector AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease System with saCas9 expressed on one vector using the strong, constitutive EF1α promoter (EF1α-hsaCas9 Two Vector AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Expression Plasmid, Cat# CASAAV200PA-1) and gRNA expressed on a separate vector using the U6 shRNA promoter (EF1α-RFP-U6-gRNA(SA) AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease gRNA Expression Plasmid, Cat# CASAAV300PA-1).
Please note the “How it Works” section below, which provides instructions for the slightly different gRNA design needed when using hsaCas9.- Deliver Cas9 in vivo
- Edit genomes in post-natal animals
- Develop gene therapies in small animal models
- Generate novel disease models
- Choose from All-in-one or Two Vector AAV-Cas9 systems
Why AAV?
With their broad tropism, the lack of disease associated with wild-type virus, ability to transduce both dividing and non-dividing cells, and long term transgene expression, recombinant AAV (rAAV) has recently become the method of choice for delivering gene therapy and genome engineering vectors to intact organisms1, 2. However, for efficient packaging, inserts into the region between rAAV’s two ITR sequences must be less than 5 kb.
Why saCas9?
The development of CRISPR/Cas9 has already revolutionized what’s possible when it comes to manipulating the genomes of even complex organisms. However, in vivo delivery via rAAV vectors has been hampered by the size of the Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9 gene (spCas9), the most widely-used form of Cas9. To overcome this problem, Ran, et al,1 characterized smaller orthologs of the Cas9 gene and found that Cas9 from Staphylococcus aureus (saCas9) performs as efficiently as spCas9 while being ~1 kb shorter, enabling insertion into rAAV vectors.
Why SBI for AAV-Cas9?
With advanced rAAV systems and a range of easy-to-use Cas9 vectors and kits, SBI has the expertise to combine these two technologies into a single, easy-to-use, and powerful system. Choose from our All-in-one or Two Vector systems to drive your in vivo genome editing studies into high gear.
Why an HR targeting vector is a recommended
Even though gene knock-outs can result from DSBs caused by Cas9 alone, SBI recommends the use of HR targeting vectors (also called HR donor vectors) for more efficient and precise mutation. HR donors can supply elements for positive or negative selection ensuring easier identification of successful mutation events. In addition, HR donors can include up to 6-8 kb of open reading frame for gene knock-ins or tagging, and, when small mutations are included in either 5’ or 3’ homology arms, can make specific, targeted gene edits.
Not sure whether you need a CRISPR/Cas9 plasmid, purified protein, or mRNA?
Use this table to choose the CRISPR/Cas9 product that’s right for you:
For This Application | In these types of cells | Use These Products |
|---|---|---|
MODIFYING ORGANISMS
| Embryos—to create transgenic animals | Injectable Cas9 mRNA & gRNA Synthesis Kits Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
| Animals models—in vivo genome editing | AAV-Cas9 Vectors Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
|
MODIFYING CELL LINES
| Cells that are transfectable | Cas9 Plasmids Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
Difficult-to-transfect cell lines:
| AAV-Cas9 Vectors Lenti Cas9 Systems |
|
SCREENING
| All cell types requiring stable Cas9 overexpression | Lenti Cas9 Systems AAVS1 Safe Harbor Site Cas9 Gene Knock-in System Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
PRE-CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
| All cell types and applications | Cas9 Nickase, available in all delivery formats Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
| SIMULTANEOUS ENGINEERING OF MULTIPLE MUTATIONS | All cell types and applications | Multiplex gRNA cloning kit, compatible with all Cas9 delivery options |
- Vasileva A and Jessberger R. Precise hit: adeno-associated virus in gene targeting. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005 Nov; 3(11):837-47. PMID: 16261169.
- Petrs-Silva H and Linden R. Advances in gene therapy technologies to treat retinitis pigmentosa. Clin Ophthalmol. 2014; 8:127–136. PMCID: PMC3878960.
- Ran, F. A. et al. In vivo genome editing using Staphylococcus aureus Nature. 2015; 520:186–191. PMCID: PMC4393360.
References
How It Works
How It Works
Using saCas9
While saCas9 is just as efficient as spCas9, a few differences between the two systems will affect gRNA design1.
- saCas9 PAM differs from spCas9 PAM
- saCas9 works most efficiently with gRNAs of 21 nt – 23 nt
Contact us with any questions on gRNA design for saCas9 or about using our AAV-Cas9 vectors by emailing tech@systembio.com.
saCas9 PAM sequences:
NNGGGT
NNGAAT
NNGAGT
To create gRNAs for AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Plasmids, use the following:
Fwd-5.1: ACCGNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN (N target sequence or gRNA sequence, 21 nts)
Rev-3.1: aaacXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX (X reverse complementary of N, 21 nts)
Example:
aavs1 gRNA for saCas9: CTGTCCCTAGTGGCCCCACTG
sa-AAVS1gRNA-5.1 ACCGCTGTCCCTAGTGGCCCCACTG
sa-AAVS1gRNA-3.1 aaacCAGTGGGGCCACTAGGGACAG
The workflow at-a-glance
- Design two DNA oligonucleotides that are sense and antisense sequences of the target DNA and are immediately upstream of a PAM sequence (see above section on creating gRNAs for AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Plasmids)
- Anneal the two oligonucleotides to generate a duplex
- Ligate the duplex into the pre-linearized All-in-one AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Plasmid
- Transform into competent cells and grow in LB/Kanamycin plate (50 µg/ml)
- Confirm positive clones by direct sequencing
- Transfect sequence-verified All-in-one construct into AAV packaging cells
- Isolate packaged All-in-one AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Plasmid using AAVanced AAV Concentration Reagent for easy, high-titer preparations
Your AAV Cas9/gRNA virus is ready for your genome editing project.
Genome engineering with CRISPR/Cas9
For general guidance on using CRISPR/Cas9 technology for genome engineering, take a look at our CRISPR/Cas9 tutorials as well as the following application notes:
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Knock-Out Application Note (PDF) »
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing Application Note (PDF) »
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Tagging Application Note (PDF) »
CRISPR/Cas9 Basics
Through careful selection of the target sequence and design of a donor plasmid for homologous recombination, you can achieve efficient and highly targeted genomic modification with CRISPR/Cas9.
The system
Cas9 protein—uses guide RNA (gRNA) to direct site-specific, double-strand DNA cleavage adjacent to a protospacer adapter motif (PAM) in the target DNA.
gRNA—RNA sequence that guides Cas9 to cleave a homologous region in the target genome. Efficient cleavage only where the gRNA homology is adjacent to a PAM.
PAM—protospacer adapter motif, NGG, is a target DNA sequence that spCas9 will cut upstream from if directed to by the gRNA.
The workflow at-a-glance
DESIGN: Select gRNA and HR donor plasmids. Choice of gRNA site and design of donor plasmid determines whether the homologous recombination event results in a knock-out, knock-in, edit, or tagging.
CONSTRUCT: Clone gRNA into all-in-one Cas9 vector. Clone 5’ and 3’ homology arms into HR donor plasmid. If creating a knock-in, clone desired gene into HR donor.
CO-TRANSFECT or CO-INJECT: Introduce Cas9, gRNA, and HR Donors into the target cells using co-transfection for plasmids, co-transduction for lentivirus, or co-injection for mRNAs.
SELECT/SCREEN: Select or screen for mutants and verify.
VALIDATE: Genotype or sequence putative mutants to verify single or biallelic conversion.
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Genome engineering with SBI’s All-in-one AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Plasmids
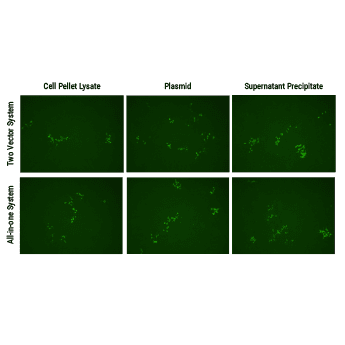
Both SBI’s all-in-one AAV-Cas9 and two-vector AAV-Cas9 systems efficiently correct a dysfunctional genomic copy of EGFP.
Starting with an Enhanced Green Fluorescent Inhibited Protein (EGIP) reporter cell line, which has an inactivated EGFP due to a premature stop codon, we designed a gRNA sequence and HR rescue donor to remove the stop codon and enable GFP expression. The gRNA sequence was inserted into either Cat # CASAAV300PA-1, EF1-RFP-U6-gRNA(SA)—the gRNA-expressing plasmid in the Two Vector AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease System (Figure 1, top panels)—or Cat # CASAAV100PA-1, the EF1α-hsaCas9-U6-gRNA(SA) All-in-one AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Plasmid (Figure 1, bottom panels).
AAV virus particles isolated from both cell lysates (Figure 1, left panels) and packaging supernatants (Figure 1, right panels) were delivered to cells with the rescue HR donor and restored EGFP expression, indicating successful genome editing.
Delivery of AAV plasmid(s) alone (Figure 1, middle panels) with HR donor also restored EGFP expression, again indicating successful genome editing.
Figure 1. Both SBI’s all-in-one AAV-Cas9 and two-vector AAV-Cas9 systems efficiently correct a dysfunctional genomic copy of EGFP. METHODS: Approximately 1 – 1.5 x 106 EGIP reporter cells were seeded into a 12-well plate for infection with isolated AAV particles (left and right panels) or transfection with plasmid (middle panels), along with the HR rescue donor. The top panels were treated with the Two Vector AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease System plus HR rescue donor designed to correct the defect in EGIP, restoring EGFP expression. The bottom panels were treated with the All-in-one AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Plasmid plus the same HR rescue donor. Three days post-infection or transfection, EGFP-positive cells can clearly be seen, indicating successful genome editing.
FAQs
Documentation
Citations
Related Products
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASAAV300PA-1 | gRNA expression vector for the Two Vector AAV SmartNuclease System, linearized AAV plasmid (EF1α-RFP-U6-gRNA(SA)) | 10 Reactions | $669 |
|
||||
Overview
Overview
Expanding your genome editing capabilities with our flexible AAV Two Vector System
Bringing together the versatile CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing system with powerful recombinant AAV (rAAV) technology, SBI’s AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease™ vectors extend genome editing capabilities to cutting edge in vivo applications.

For situations where you would like to introduce saCas9 and gRNA separately, SBI offers a Two Vector AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease System with saCas9 expressed on one vector using the strong, constitutive EF1α promoter (EF1α-hsaCas9 Two Vector AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Expression Plasmid, Cat# CASAAV200PA-1) and gRNA expressed on a separate vector using the U6 shRNA promoter (EF1α-RFP-U6-gRNA(SA) AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease gRNA Expression Plasmid, Cat# CASAAV300PA-1).
Please note the “How it Works” section below, which provides instructions for the slightly different gRNA design needed when using hsaCas9.- Deliver Cas9 in vivo
- Edit genomes in post-natal animals
- Develop gene therapies in small animal models
- Generate novel disease models
- Choose from All-in-one or Two Vector AAV-Cas9 systems
Why AAV?
With their broad tropism, the lack of disease associated with wild-type virus, ability to transduce both dividing and non-dividing cells, and long term transgene expression, recombinant AAV (rAAV) has recently become the method of choice for delivering gene therapy and genome engineering vectors to intact organisms1, 2. However, for efficient packaging, inserts into the region between rAAV’s two ITR sequences must be less than 5 kb.
Why saCas9?
The development of CRISPR/Cas9 has already revolutionized what’s possible when it comes to manipulating the genomes of even complex organisms. However, in vivo delivery via rAAV vectors has been hampered by the size of the Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9 gene (spCas9), the most widely-used form of Cas9. To overcome this problem, Ran, et al,1 characterized smaller orthologs of the Cas9 gene and found that Cas9 from Staphylococcus aureus (saCas9) performs as efficiently as spCas9 while being ~1 kb shorter, enabling insertion into rAAV vectors.
Why SBI for AAV-Cas9?
With advanced rAAV systems and a range of easy-to-use Cas9 vectors and kits, SBI has the expertise to combine these two technologies into a single, easy-to-use, and powerful system. Choose from our All-in-one or Two Vector systems to drive your in vivo genome editing studies into high gear.
Why an HR targeting vector is a recommended
Even though gene knock-outs can result from DSBs caused by Cas9 alone, SBI recommends the use of HR targeting vectors (also called HR donor vectors) for more efficient and precise mutation. HR donors can supply elements for positive or negative selection ensuring easier identification of successful mutation events. In addition, HR donors can include up to 6-8 kb of open reading frame for gene knock-ins or tagging, and, when small mutations are included in either 5’ or 3’ homology arms, can make specific, targeted gene edits.
Not sure whether you need a CRISPR/Cas9 plasmid, purified protein, or mRNA?
Use this table to choose the CRISPR/Cas9 product that’s right for you:
For This Application | In these types of cells | Use These Products |
|---|---|---|
MODIFYING ORGANISMS
| Embryos—to create transgenic animals | Injectable Cas9 mRNA & gRNA Synthesis Kits Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
| Animals models—in vivo genome editing | AAV-Cas9 Vectors Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
|
MODIFYING CELL LINES
| Cells that are transfectable | Cas9 Plasmids Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
Difficult-to-transfect cell lines:
| AAV-Cas9 Vectors Lenti Cas9 Systems |
|
SCREENING
| All cell types requiring stable Cas9 overexpression | Lenti Cas9 Systems AAVS1 Safe Harbor Site Cas9 Gene Knock-in System Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
PRE-CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
| All cell types and applications | Cas9 Nickase, available in all delivery formats Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
| SIMULTANEOUS ENGINEERING OF MULTIPLE MUTATIONS | All cell types and applications | Multiplex gRNA cloning kit, compatible with all Cas9 delivery options |
- Vasileva A and Jessberger R. Precise hit: adeno-associated virus in gene targeting. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005 Nov; 3(11):837-47. PMID: 16261169.
- Petrs-Silva H and Linden R. Advances in gene therapy technologies to treat retinitis pigmentosa. Clin Ophthalmol. 2014; 8:127–136. PMCID: PMC3878960.
- Ran, F. A. et al. In vivo genome editing using Staphylococcus aureus Nature. 2015; 520:186–191. PMCID: PMC4393360.
References
How It Works
How It Works
Using saCas9
While saCas9 is just as efficient as spCas9, a few differences between the two systems will affect gRNA design1.
- saCas9 PAM differs from spCas9 PAM
- saCas9 works most efficiently with gRNAs of 21 nt – 23 nt
Contact us with any questions on gRNA design for saCas9 or about using our AAV-Cas9 vectors by emailing tech@systembio.com.
saCas9 PAM sequences:
NNGGGT
NNGAAT
NNGAGT
To create gRNAs for AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Plasmids, use the following:
Fwd-5.1: ACCGNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN (N target sequence or gRNA sequence, 21 nts)
Rev-3.1: aaacXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX (X reverse complementary of N, 21 nts)
Example:
aavs1 gRNA for saCas9: CTGTCCCTAGTGGCCCCACTG
sa-AAVS1gRNA-5.1 ACCGCTGTCCCTAGTGGCCCCACTG
sa-AAVS1gRNA-3.1 aaacCAGTGGGGCCACTAGGGACAG
The workflow at-a-glance
- Design two DNA oligonucleotides that are sense and antisense sequences of the target DNA and are immediately upstream of a PAM sequence (see above section on creating gRNAs for AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Plasmids)
- Anneal the two oligonucleotides to generate a duplex
- Ligate the duplex into the pre-linearized All-in-one AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Plasmid
- Transform into competent cells and grow in LB/Kanamycin plate (50 µg/ml)
- Confirm positive clones by direct sequencing
- Transfect sequence-verified All-in-one construct into AAV packaging cells
- Isolate packaged All-in-one AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Plasmid using AAVanced AAV Concentration Reagent for easy, high-titer preparations
Your AAV Cas9/gRNA virus is ready for your genome editing project.
Genome engineering with CRISPR/Cas9
For general guidance on using CRISPR/Cas9 technology for genome engineering, take a look at our CRISPR/Cas9 tutorials as well as the following application notes:
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Knock-Out Application Note (PDF) »
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing Application Note (PDF) »
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Tagging Application Note (PDF) »
CRISPR/Cas9 Basics
Through careful selection of the target sequence and design of a donor plasmid for homologous recombination, you can achieve efficient and highly targeted genomic modification with CRISPR/Cas9.
The system
Cas9 protein—uses guide RNA (gRNA) to direct site-specific, double-strand DNA cleavage adjacent to a protospacer adapter motif (PAM) in the target DNA.
gRNA—RNA sequence that guides Cas9 to cleave a homologous region in the target genome. Efficient cleavage only where the gRNA homology is adjacent to a PAM.
PAM—protospacer adapter motif, NGG, is a target DNA sequence that spCas9 will cut upstream from if directed to by the gRNA.
The workflow at-a-glance
DESIGN: Select gRNA and HR donor plasmids. Choice of gRNA site and design of donor plasmid determines whether the homologous recombination event results in a knock-out, knock-in, edit, or tagging.
CONSTRUCT: Clone gRNA into all-in-one Cas9 vector. Clone 5’ and 3’ homology arms into HR donor plasmid. If creating a knock-in, clone desired gene into HR donor.
CO-TRANSFECT or CO-INJECT: Introduce Cas9, gRNA, and HR Donors into the target cells using co-transfection for plasmids, co-transduction for lentivirus, or co-injection for mRNAs.
SELECT/SCREEN: Select or screen for mutants and verify.
VALIDATE: Genotype or sequence putative mutants to verify single or biallelic conversion.
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Genome engineering with SBI’s All-in-one AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Plasmids
Both SBI’s all-in-one AAV-Cas9 and two-vector AAV-Cas9 systems efficiently correct a dysfunctional genomic copy of EGFP.
Starting with an Enhanced Green Fluorescent Inhibited Protein (EGIP) reporter cell line, which has an inactivated EGFP due to a premature stop codon, we designed a gRNA sequence and HR rescue donor to remove the stop codon and enable GFP expression. The gRNA sequence was inserted into either Cat # CASAAV300PA-1, EF1-RFP-U6-gRNA(SA)—the gRNA-expressing plasmid in the Two Vector AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease System (Figure 1, top panels)—or Cat # CASAAV100PA-1, the EF1α-hsaCas9-U6-gRNA(SA) All-in-one AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Plasmid (Figure 1, bottom panels).
AAV virus particles isolated from both cell lysates (Figure 1, left panels) and packaging supernatants (Figure 1, right panels) were delivered to cells with the rescue HR donor and restored EGFP expression, indicating successful genome editing.
Delivery of AAV plasmid(s) alone (Figure 1, middle panels) with HR donor also restored EGFP expression, again indicating successful genome editing.
Figure 1. Both SBI’s all-in-one AAV-Cas9 and two-vector AAV-Cas9 systems efficiently correct a dysfunctional genomic copy of EGFP. METHODS: Approximately 1 – 1.5 x 106 EGIP reporter cells were seeded into a 12-well plate for infection with isolated AAV particles (left and right panels) or transfection with plasmid (middle panels), along with the HR rescue donor. The top panels were treated with the Two Vector AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease System plus HR rescue donor designed to correct the defect in EGIP, restoring EGFP expression. The bottom panels were treated with the All-in-one AAV Cas9 SmartNuclease Plasmid plus the same HR rescue donor. Three days post-infection or transfection, EGFP-positive cells can clearly be seen, indicating successful genome editing.