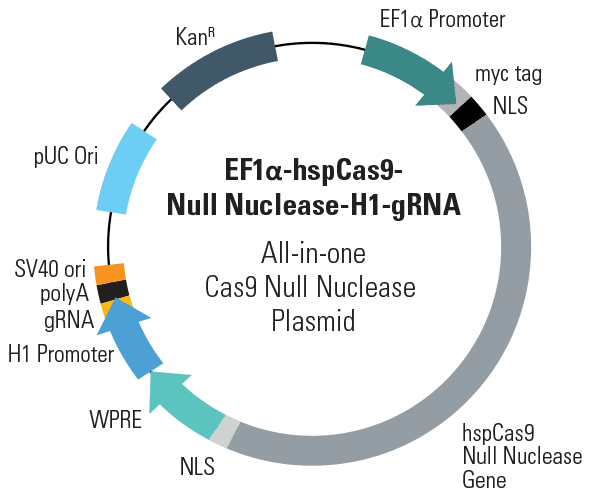
EF1α-hspCas9-DM-H1-gRNA All-in-one Cas9 Null Nuclease Plasmid (circular)
- Conveniently deliver Cas9 Null Nuclease and gRNA with a single vector
- Drive Cas9 Null Nuclease expression with the EF1α promoter, which provides medium expression levels in most cell types, including primary cells and stem cells
- Express gRNA from the H1 promoter for maximum specificity and choice of targets
- Ensure efficient import of Cas9 Null Nuclease to the nucleus with N-term and C-term nuclear localization signals (NLSs)
- Boost Cas9 Null Nuclease gene expression and stabilize the transcript via the WPRE regulatory element after the C-term NLS
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS805A-1 | All-in-one Cas9 Null Nuclease: EF1α-hspCas9-DM-H1-gRNA NullNuclease vector | 10 µg | $751 |
|
||||
Overview
Overview
Speed your studies with ready-made controls
When you’d like an inactive control for your genome engineering studies, SBI offers the EF1α-hspCas9-DM-H1-gRNA All-in-one Cas9 Null Nuclease Plasmid (circular), which is deficient in DNA cleavage and nickase activity. This plasmid and all of our first-generation All-in-one Cas9 Plasmids are now available in a circular, non-linearized format.
- Conveniently deliver Cas9 Null Nuclease and gRNA with a single vector
- Drive Cas9 Null Nuclease expression with the EF1α promoter, which provides medium expression levels in most cell types, including primary cells and stem cells
- Express gRNA from the H1 promoter for maximum specificity and choice of targets
- Ensure efficient import of Cas9 Null Nuclease to the nucleus with N-term and C-term nuclear localization signals (NLSs)
- Boost Cas9 Null Nuclease gene expression and stabilize the transcript via the WPRE regulatory element after the C-term NLS
- Easily detect and/or purify the Cas9 Null Nuclease protein with the N-term myc-tag
As with all of our Cas9 delivery options, the EF1α-hspCas9-DM-H1-gRNA All-in-one Cas9 Null Nuclease is functionally validated and comes backed by our expert technical support team—if you’ve got a genome engineering question just ask by emailing tech@systembio.com.
Why an HR targeting vector is a recommended
Even though gene knock-outs can result from DSBs caused by Cas9 alone, SBI recommends the use of HR targeting vectors (also called HR donor vectors) for more efficient and precise mutation. HR donors can supply elements for positive or negative selection ensuring easier identification of successful mutation events. In addition, HR donors can include up to 6-8 kb of open reading frame for gene knock-ins or tagging, and, when small mutations are included in either 5’ or 3’ homology arms, can make specific, targeted gene edits.
Not sure whether you need a CRISPR/Cas9 plasmid, purified protein, or mRNA?
Use this table to choose the CRISPR/Cas9 product that’s right for you.
For This Application | In these types of cells | Use These Products |
|---|---|---|
MODIFYING ORGANISMS
| Embryos—to create transgenic animals | Injectable Cas9 mRNA & gRNA Synthesis Kits Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
| Animals models—in vivo genome editing | AAV-Cas9 Vectors Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
|
MODIFYING CELL LINES
| Cells that are transfectable | Cas9 Plasmids Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
Difficult-to-transfect cell lines:
| AAV-Cas9 Vectors Lenti Cas9 Systems |
|
SCREENING
| All cell types requiring stable Cas9 overexpression | Lenti Cas9 Systems AAVS1 Safe Harbor Site Cas9 Gene Knock-in System Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
PRE-CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
| All cell types and applications | Cas9 Nickase, available in all delivery formats Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
| SIMULTANEOUS ENGINEERING OF MULTIPLE MUTATIONS | All cell types and applications | Multiplex gRNA cloning kit, compatible with all Cas9 delivery options |
References
How It Works
How It Works
Genome engineering with CRISPR/Cas9
For general guidance on using CRISPR/Cas9 technology for genome engineering, take a look at our CRISPR/Cas9 tutorials as well as the following application notes:
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Knock-Out Application Note (PDF) »
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing Application Note (PDF) »
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Tagging Application Note (PDF) »
CRISPR/Cas9 Basics
Through careful selection of the target sequence and design of a donor plasmid for homologous recombination, you can achieve efficient and highly targeted genomic modification with CRISPR/Cas9.
The system
Cas9 protein—uses guide RNA (gRNA) to direct site-specific, double-strand DNA cleavage adjacent to a protospacer adapter motif (PAM) in the target DNA.
gRNA—RNA sequence that guides Cas9 to cleave a homologous region in the target genome. Efficient cleavage only where the gRNA homology is adjacent to a PAM.
PAM—protospacer adapter motif, NGG, is a target DNA sequence that spCas9 will cut upstream from if directed to by the gRNA.
The workflow at-a-glance
DESIGN: Select gRNA and HR donor plasmids. Choice of gRNA site and design of donor plasmid determines whether the homologous recombination event results in a knock-out knock-in, edit, or tagging.
CONSTRUCT: Clone gRNA into all-in-one Cas9 vector. Clone 5’ and 3’ homology arms into HR donor plasmid. If creating a knock-in, clone desired gene into HR donor.
CO-TRANSFECT or CO-INJECT: Introduce Cas9, gRNA, and HR Donors into the target cells using co-transfection for plasmids, co-transduction for lentivirus, or co-injection for mRNAs.
SELECT/SCREEN: Select or screen for mutants and verify.
VALIDATE: Genotype or sequence putative mutants to verify single or biallelic conversion.
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Validating SBI’s CRISPR/Cas9 SmartNickase and Null Nuclease Vectors
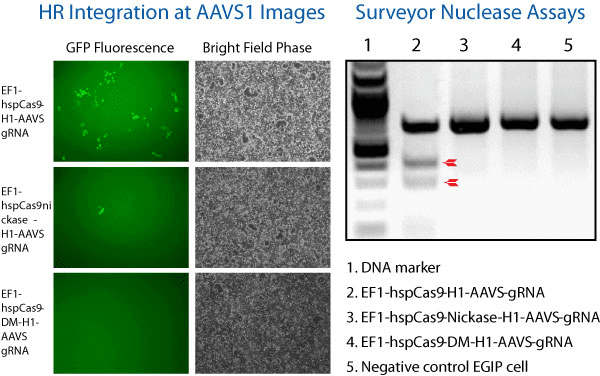
Figure 1. The All-in-one Cas9 Null Nuclease Vector shows no genome editing activity. We compared the activity of wild-type Cas9 (EF1α-hspCas9-H1-gRNA All-in-one SmartNuclease Plasmid, Cat.# CAS900A-1), Cas9 SmartNickase (EF1α-hspCas9-nickase-H1-gRNA All-in-one SmartNickase Plasmid, Cat.# CAS800A-1), and Cas9 Null Nuclease (EF1α-hspCas9-DM-H1-gRNA All-in-one Cas9 Null Nuclease Plasmid, Cat.# CAS805A-1) to insert a GFP reporter at the AAVS1 site through the use of AAVS1-targeting gRNA and an AAVS1-targeting HR Targeting Vector (AAVS1 Safe Harbor cDNA/miRNA Targeting HR Donor Vector (pAAVS1D-PGK-MCS-EF1α-copGFPpuro), Cat.# GE602A-1).
(Left panel) Fluorescence (left-most column) and bright field (right-most column) microscopy showing that both Cas9 SmartNuclease (top set) and Cas9 SmartNickase (middle set) are able to insert GFP into the genome, whereas the Cas9 Null Nuclease is not (bottom set).
(Right panel) A Surveyor Nuclease Assay corroborates the lack of genome editing capabilities of the Cas9 Null Nuclease. The lack of cleavage seen in the SmartNickase lane is likely due to the lower frequency of GFP insertion.
FAQs
Resources
Citations
Related Products
Products
| Catalog Number | Description | Size | Price | Quantity | Add to Cart | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS805A-1 | All-in-one Cas9 Null Nuclease: EF1α-hspCas9-DM-H1-gRNA NullNuclease vector | 10 µg | $751 |
|
||||
Overview
Overview
Speed your studies with ready-made controls
When you’d like an inactive control for your genome engineering studies, SBI offers the EF1α-hspCas9-DM-H1-gRNA All-in-one Cas9 Null Nuclease Plasmid (circular), which is deficient in DNA cleavage and nickase activity. This plasmid and all of our first-generation All-in-one Cas9 Plasmids are now available in a circular, non-linearized format.

- Conveniently deliver Cas9 Null Nuclease and gRNA with a single vector
- Drive Cas9 Null Nuclease expression with the EF1α promoter, which provides medium expression levels in most cell types, including primary cells and stem cells
- Express gRNA from the H1 promoter for maximum specificity and choice of targets
- Ensure efficient import of Cas9 Null Nuclease to the nucleus with N-term and C-term nuclear localization signals (NLSs)
- Boost Cas9 Null Nuclease gene expression and stabilize the transcript via the WPRE regulatory element after the C-term NLS
- Easily detect and/or purify the Cas9 Null Nuclease protein with the N-term myc-tag
As with all of our Cas9 delivery options, the EF1α-hspCas9-DM-H1-gRNA All-in-one Cas9 Null Nuclease is functionally validated and comes backed by our expert technical support team—if you’ve got a genome engineering question just ask by emailing tech@systembio.com.
Why an HR targeting vector is a recommended
Even though gene knock-outs can result from DSBs caused by Cas9 alone, SBI recommends the use of HR targeting vectors (also called HR donor vectors) for more efficient and precise mutation. HR donors can supply elements for positive or negative selection ensuring easier identification of successful mutation events. In addition, HR donors can include up to 6-8 kb of open reading frame for gene knock-ins or tagging, and, when small mutations are included in either 5’ or 3’ homology arms, can make specific, targeted gene edits.
Not sure whether you need a CRISPR/Cas9 plasmid, purified protein, or mRNA?
Use this table to choose the CRISPR/Cas9 product that’s right for you.
For This Application | In these types of cells | Use These Products |
|---|---|---|
MODIFYING ORGANISMS
| Embryos—to create transgenic animals | Injectable Cas9 mRNA & gRNA Synthesis Kits Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
| Animals models—in vivo genome editing | AAV-Cas9 Vectors Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
|
MODIFYING CELL LINES
| Cells that are transfectable | Cas9 Plasmids Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
Difficult-to-transfect cell lines:
| AAV-Cas9 Vectors Lenti Cas9 Systems |
|
SCREENING
| All cell types requiring stable Cas9 overexpression | Lenti Cas9 Systems AAVS1 Safe Harbor Site Cas9 Gene Knock-in System Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
PRE-CLINICAL APPLICATIONS
| All cell types and applications | Cas9 Nickase, available in all delivery formats Cas9 Protein EGFP-labeled Cas9 Protein |
| SIMULTANEOUS ENGINEERING OF MULTIPLE MUTATIONS | All cell types and applications | Multiplex gRNA cloning kit, compatible with all Cas9 delivery options |
References
How It Works
How It Works
Genome engineering with CRISPR/Cas9
For general guidance on using CRISPR/Cas9 technology for genome engineering, take a look at our CRISPR/Cas9 tutorials as well as the following application notes:
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Knock-Out Application Note (PDF) »
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing Application Note (PDF) »
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Tagging Application Note (PDF) »
CRISPR/Cas9 Basics
Through careful selection of the target sequence and design of a donor plasmid for homologous recombination, you can achieve efficient and highly targeted genomic modification with CRISPR/Cas9.
The system
Cas9 protein—uses guide RNA (gRNA) to direct site-specific, double-strand DNA cleavage adjacent to a protospacer adapter motif (PAM) in the target DNA.
gRNA—RNA sequence that guides Cas9 to cleave a homologous region in the target genome. Efficient cleavage only where the gRNA homology is adjacent to a PAM.
PAM—protospacer adapter motif, NGG, is a target DNA sequence that spCas9 will cut upstream from if directed to by the gRNA.
The workflow at-a-glance
DESIGN: Select gRNA and HR donor plasmids. Choice of gRNA site and design of donor plasmid determines whether the homologous recombination event results in a knock-out knock-in, edit, or tagging.
CONSTRUCT: Clone gRNA into all-in-one Cas9 vector. Clone 5’ and 3’ homology arms into HR donor plasmid. If creating a knock-in, clone desired gene into HR donor.
CO-TRANSFECT or CO-INJECT: Introduce Cas9, gRNA, and HR Donors into the target cells using co-transfection for plasmids, co-transduction for lentivirus, or co-injection for mRNAs.
SELECT/SCREEN: Select or screen for mutants and verify.
VALIDATE: Genotype or sequence putative mutants to verify single or biallelic conversion.
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Validating SBI’s CRISPR/Cas9 SmartNickase and Null Nuclease Vectors
Figure 1. The All-in-one Cas9 Null Nuclease Vector shows no genome editing activity. We compared the activity of wild-type Cas9 (EF1α-hspCas9-H1-gRNA All-in-one SmartNuclease Plasmid, Cat.# CAS900A-1), Cas9 SmartNickase (EF1α-hspCas9-nickase-H1-gRNA All-in-one SmartNickase Plasmid, Cat.# CAS800A-1), and Cas9 Null Nuclease (EF1α-hspCas9-DM-H1-gRNA All-in-one Cas9 Null Nuclease Plasmid, Cat.# CAS805A-1) to insert a GFP reporter at the AAVS1 site through the use of AAVS1-targeting gRNA and an AAVS1-targeting HR Targeting Vector (AAVS1 Safe Harbor cDNA/miRNA Targeting HR Donor Vector (pAAVS1D-PGK-MCS-EF1α-copGFPpuro), Cat.# GE602A-1).
(Left panel) Fluorescence (left-most column) and bright field (right-most column) microscopy showing that both Cas9 SmartNuclease (top set) and Cas9 SmartNickase (middle set) are able to insert GFP into the genome, whereas the Cas9 Null Nuclease is not (bottom set).
(Right panel) A Surveyor Nuclease Assay corroborates the lack of genome editing capabilities of the Cas9 Null Nuclease. The lack of cleavage seen in the SmartNickase lane is likely due to the lower frequency of GFP insertion.